Earth Now Dashboard
Overview
NASA satellites provide data on Earth's land, ecosystems, water, air temperature, and climate - and have done so for more than 50 years. Earth information from space supports decision makers, partners, and people in developing the tools they need to mitigate, adapth, and respond to our changing planet.
The visualizations featured on this dashboard show the latest imagery available.
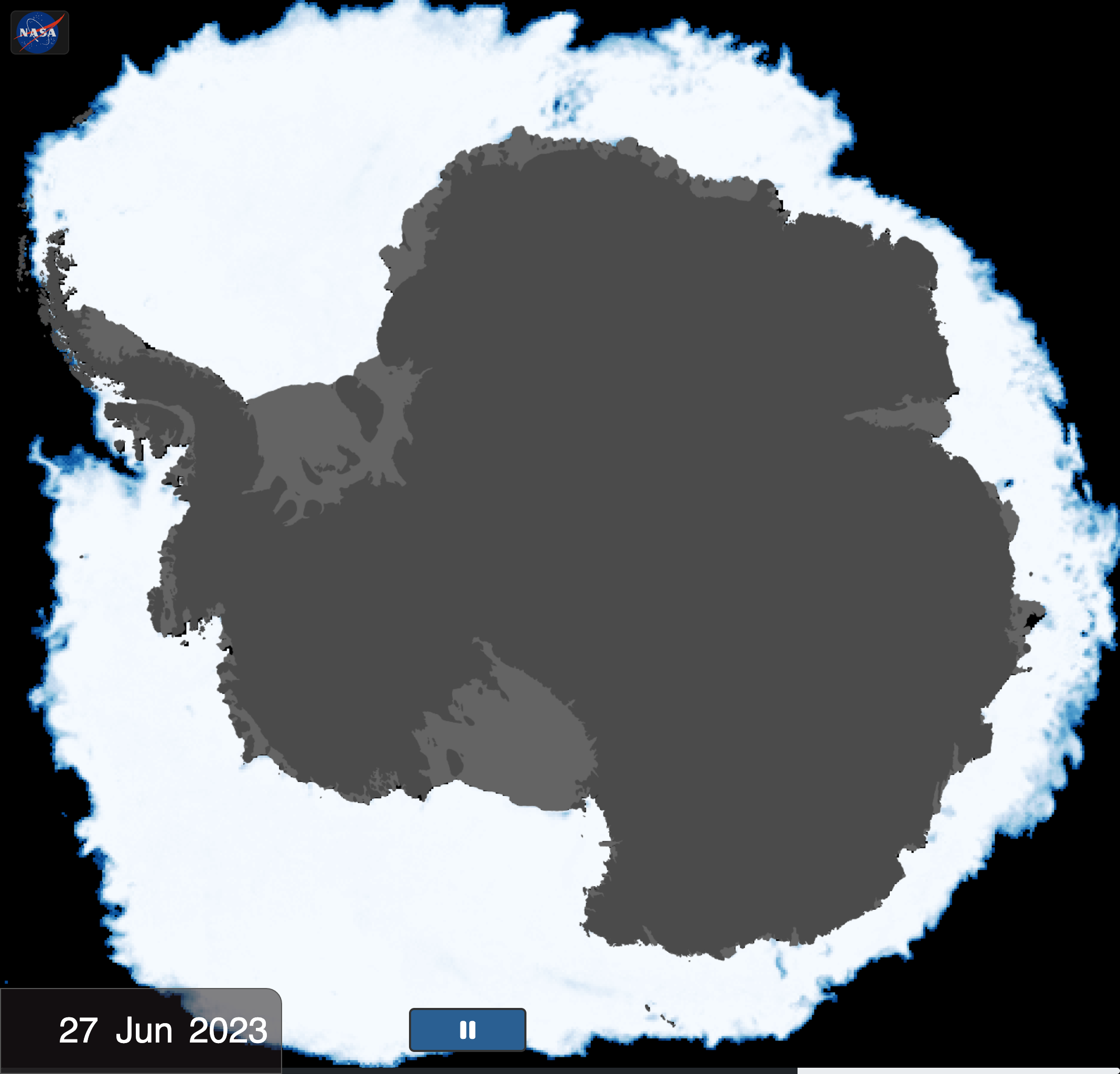
Worldview Satellite Observations - First Cycle
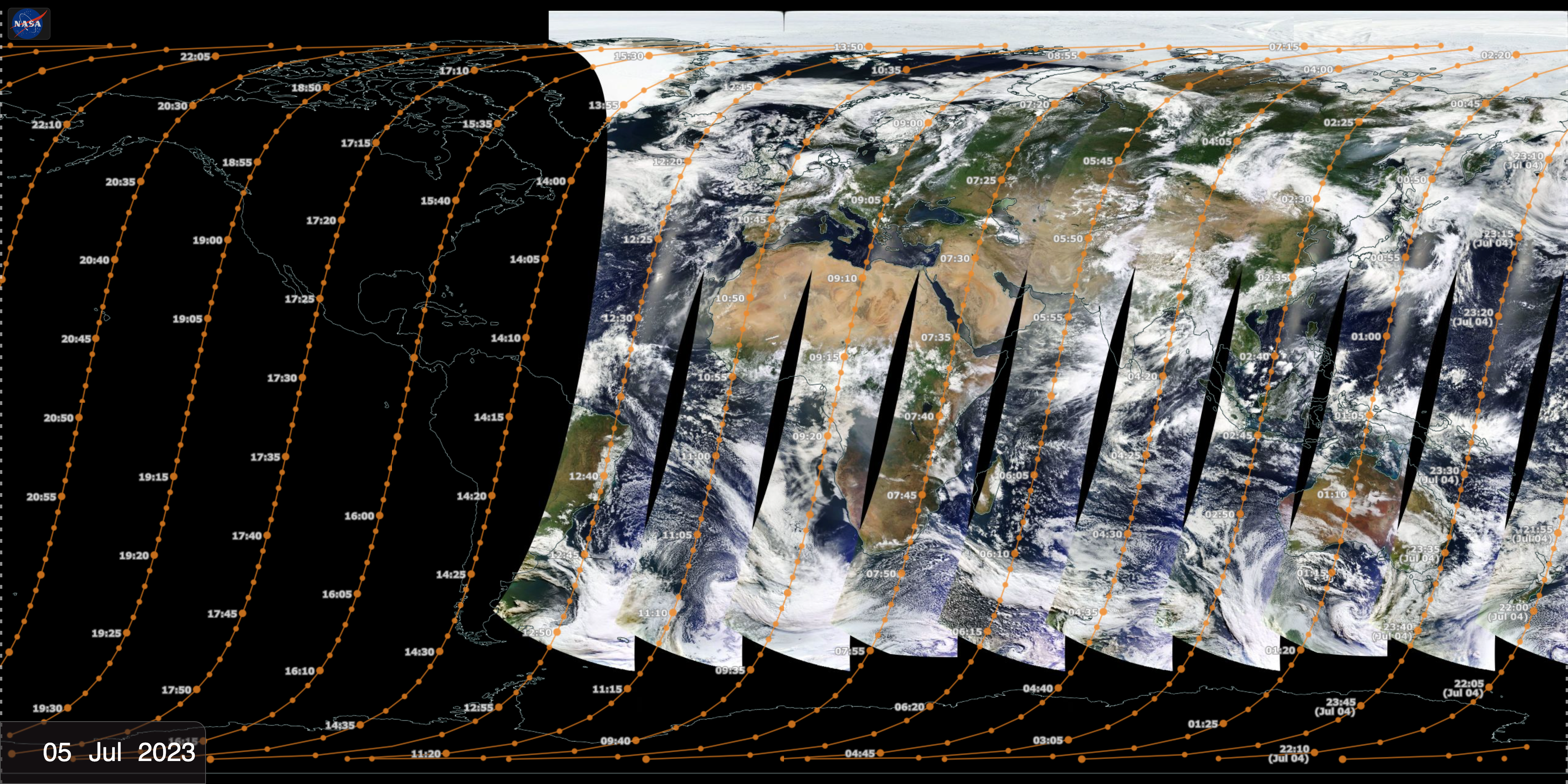
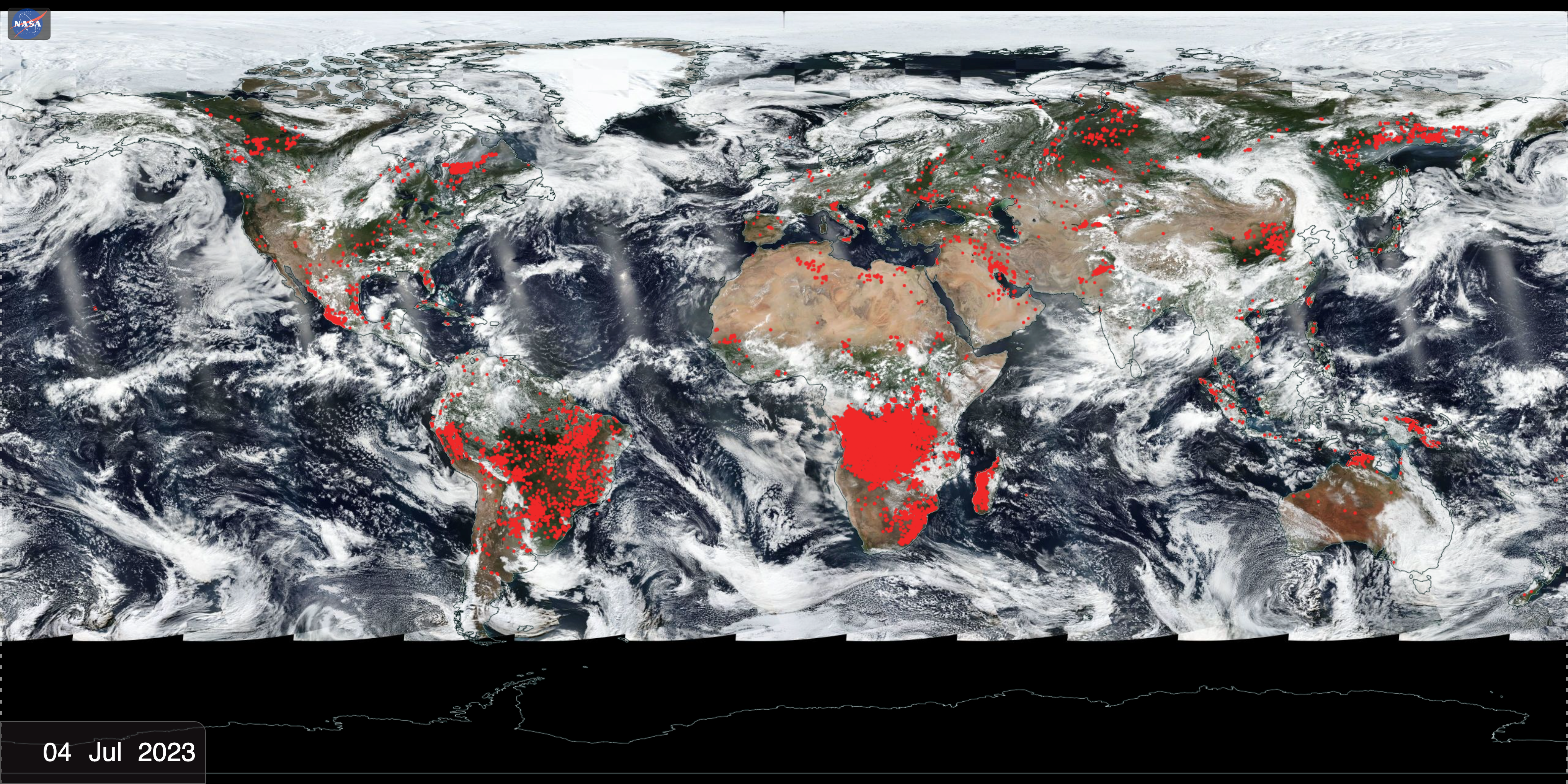
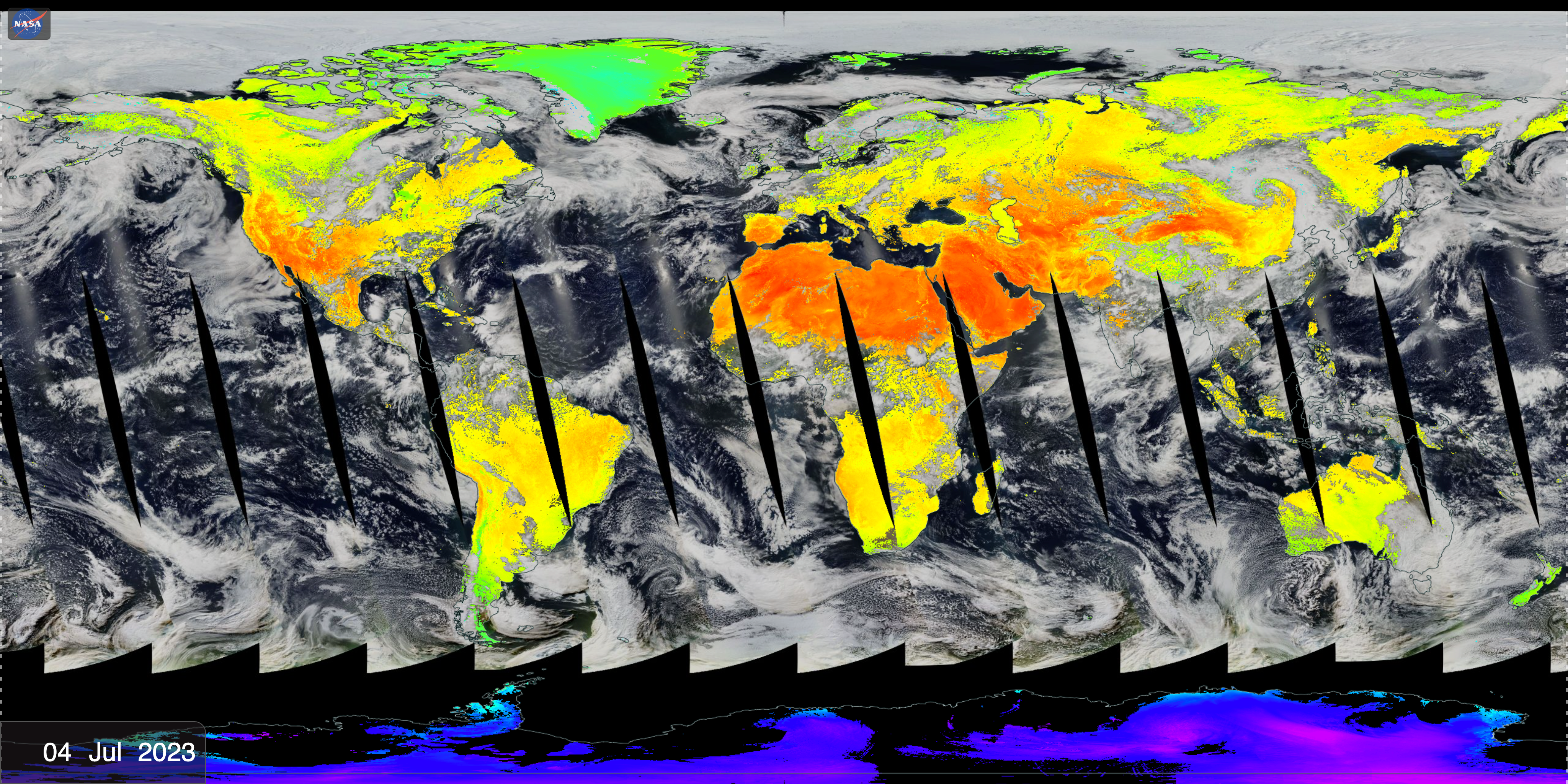
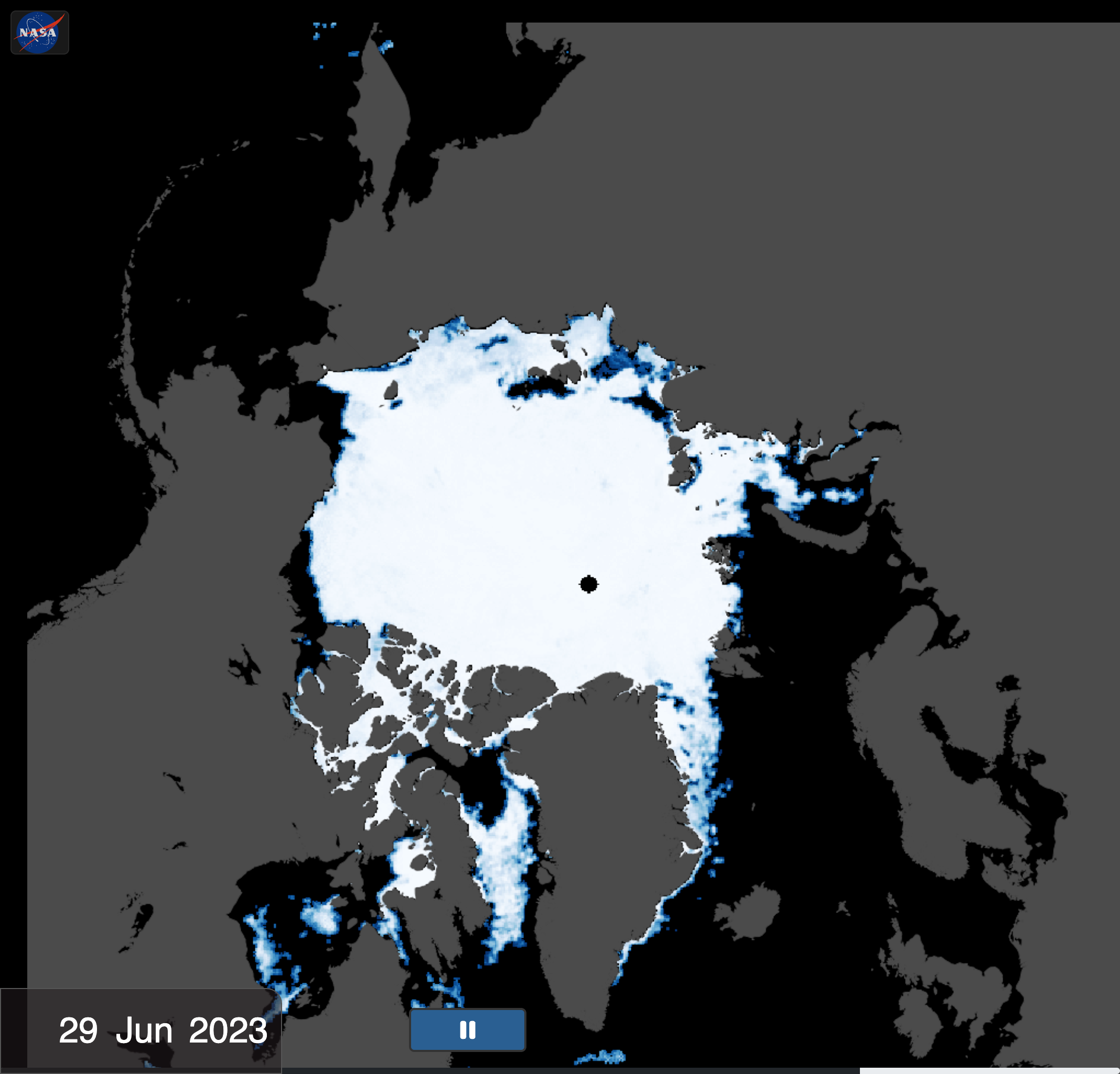
The first cycle of the Earth Now dashboard shows a set of near real-time satellite observations, provided by NASA's Worldview team. These satellite data products are generally captured within the previous three hours and are created in an expedited manner to support forecasting and monitoring of natural hazards and disasters, to assess air quality and support agricultural needs, to facilitate improved weather prediction, and to help ensure homeland security. While the displayed NASA satellite missions were originally designed for scientific research, they have been adapted to also support time sensitive applications through NASA’s Land, Atmosphere Near real-time Capability (LANCE).
Worldview Satellite Observations - Second Cycle
The second cycle of the Earth Now dashboad shows a set of recent observations covering the globe, provided by NASA's Worldview.
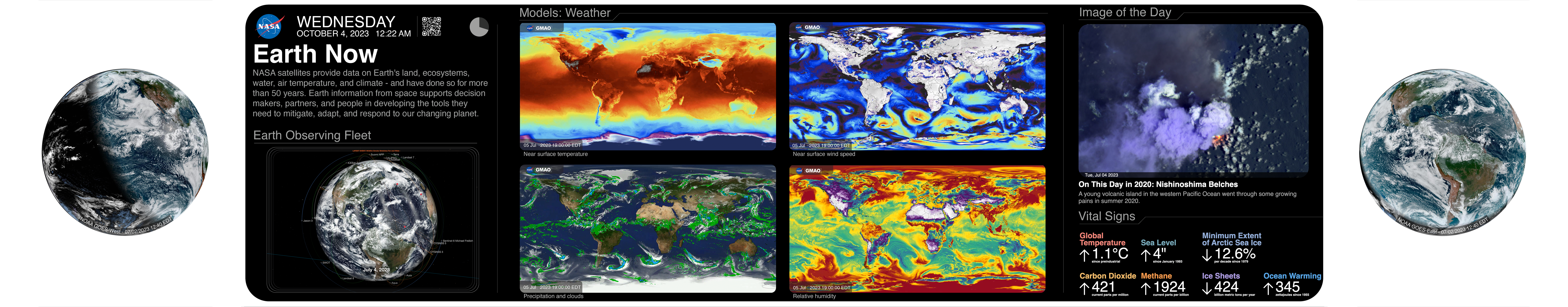
Models: Weather
Weather models begin their forecasts by integrating observations from ground stations, aircraft, balloons, and a growing constellation of Earth observing satellites to estimate the most realistic atmospheric state. The Goddard Earth Observing System Forward Processing (GEOS-FP) system is a research model maintained by NASA’s Global Modeling and Assimilation Office to demonstrate innovative new ways to use satellite data to improve predictions of weather, air quality, and greenhouse gases and to help NASA collect new observations of our home planet.
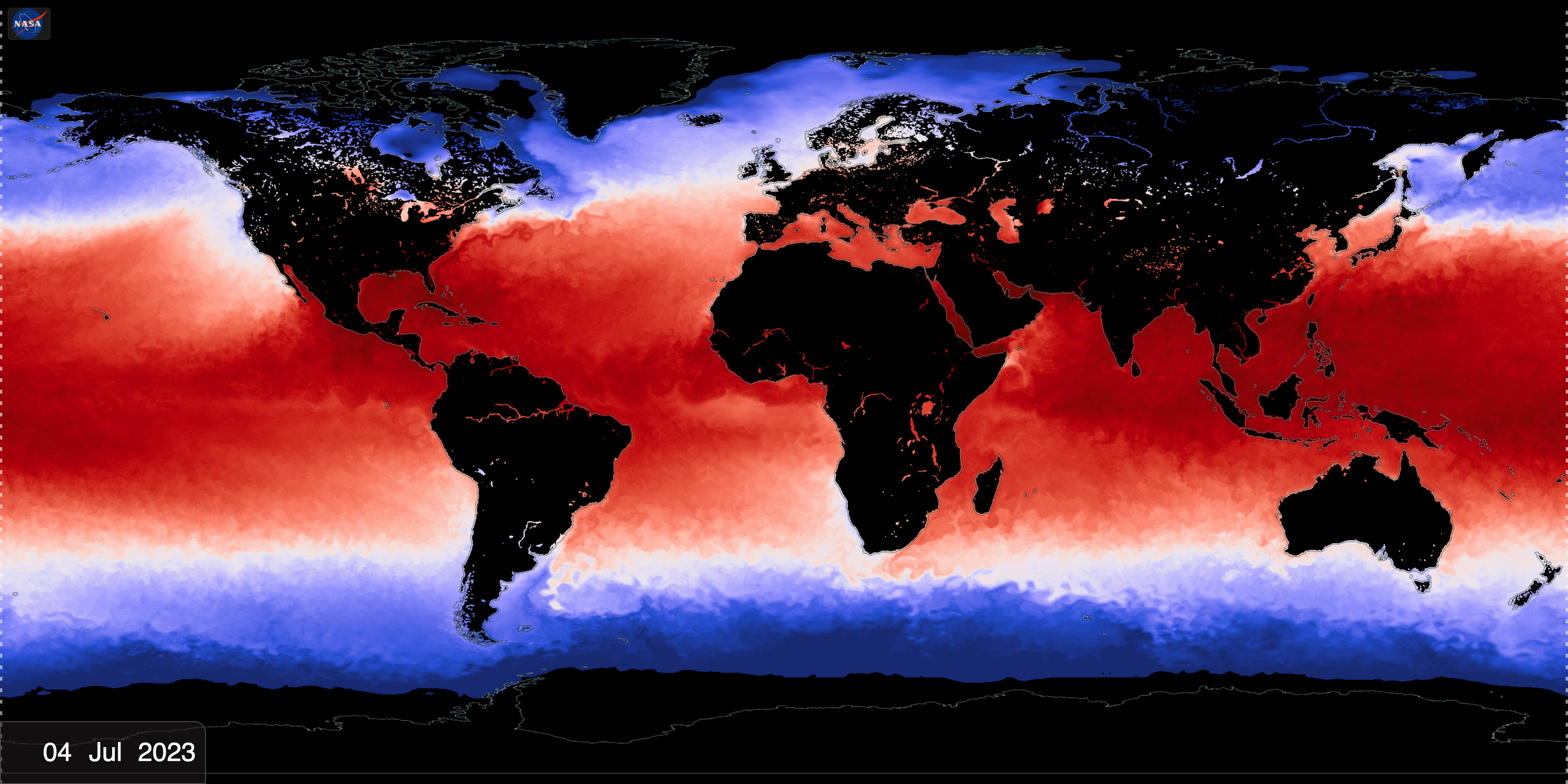
GEOS-FP Near Surface Temperature
Go to this pageNear surface temperature is calculated by sampling 3-D atmospheric fields from NASA’s GEOS-FP system 3 meters above Earth’s surface. GEOS-FP combines millions of weather observations with a predictive model to create a global best estimate of weather conditions that are used to begin a forecast. || MC01_stage3_GMAO_near_surface_temperature_2048x1024_en.00001_print.jpg (1024x512) [159.8 KB] || MC01_stage3_GMAO_near_surface_temperature_2048x1024_en.00001_searchweb.png (320x180) [91.8 KB] || MC01_stage3_GMAO_near_surface_temperature_2048x1024_en.00001_thm.png (80x40) [6.9 KB] || MC01_stage3_GMAO_near_surface_temperature_2048x1024_en.mp4 (2048x1024) [31.0 MB] || MC01_stage3_GMAO_near_surface_temperature_2048x1024_en-hwtool (2048x1024) [373 Item(s)] ||
GEOS-FP Near Surface Wind Speed
Go to this pageNear surface wind speed is calculated by sampling 3-D atmospheric fields from NASA’s GEOS-FP system 10 meters above Earth’s surface. GEOS-FP combines millions of weather observations with a predictive model to create a global best estimate of weather conditions that are used to begin a forecast. || MC02_stage3_GMAO_near_surface_wind_2048x1024_en.00001_print.jpg (1024x512) [310.1 KB] || MC02_stage3_GMAO_near_surface_wind_2048x1024_en.00001_searchweb.png (180x320) [130.9 KB] || MC02_stage3_GMAO_near_surface_wind_2048x1024_en.00001_thm.png (80x40) [8.8 KB] || MC02_stage3_GMAO_near_surface_wind_2048x1024_en.mp4 (2048x1024) [65.0 MB] || MC02_stage3_GMAO_near_surface_wind_2048x1024_en-hwtool (2048x1024) [373 Item(s)] ||
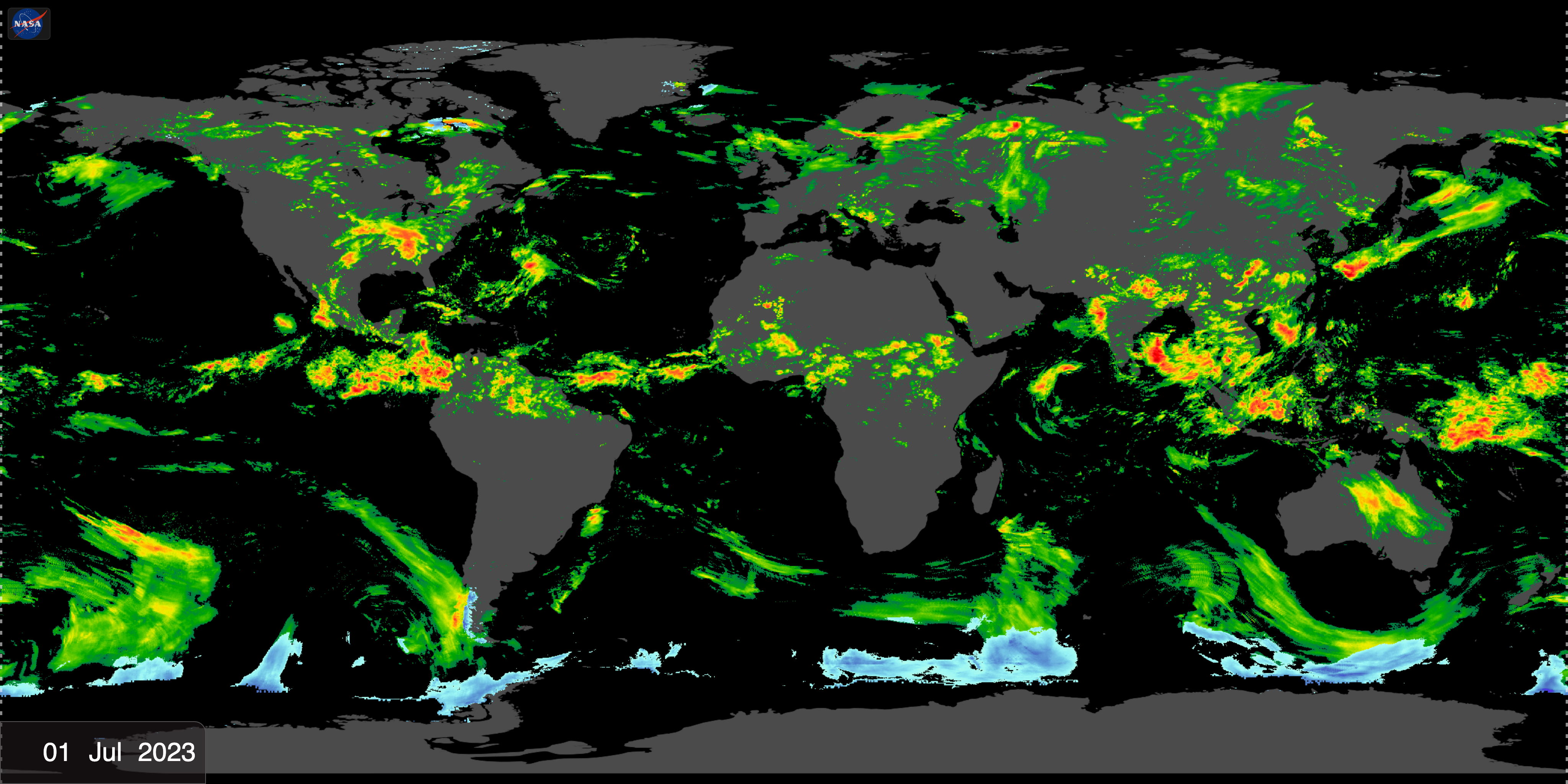
GEOS-FP Precipitation and Clouds
Go to this pagePrecipitation and clouds are calculated using fields from NASA’s GEOS-FP system. GEOS-FP combines millions of weather observations with a predictive model to create a global best estimate of weather conditions, which can be used to estimate the formation of clouds along with rain and snowfall. || MC03_stage3_GMAO_precipitation_2048x1024_en.00001_print.jpg (1024x512) [279.9 KB] || MC03_stage3_GMAO_precipitation_2048x1024_en.00001_searchweb.png (320x180) [109.4 KB] || MC03_stage3_GMAO_precipitation_2048x1024_en.00001_thm.png (80x40) [7.6 KB] || MC03_stage3_GMAO_precipitation_2048x1024_en.mp4 (2048x1024) [82.1 MB] || MC03_stage3_GMAO_precipitation_2048x1024_en-hwtool (2048x1024) [373 Item(s)] ||
GEOS-FP Relative Humidity
Go to this pageRelative humidity is calculated using temperature and moisture fields from NASA’s GEOS-FP system. GEOS-FP combines millions of weather observations with a predictive model to create a global best estimate of weather conditions that are used to begin a forecast. || MC04_stage3_GMAO_relative_humidity_2048x1024_en.00001_print.jpg (1024x512) [357.6 KB] || MC04_stage3_GMAO_relative_humidity_2048x1024_en.00001_searchweb.png (320x180) [126.2 KB] || MC04_stage3_GMAO_relative_humidity_2048x1024_en.00001_thm.png (80x40) [8.4 KB] || MC04_stage3_GMAO_relative_humidity_2048x1024_en.mp4 (2048x1024) [70.2 MB] || MC04_stage3_GMAO_relative_humidity_2048x1024_en-hwtool (2048x1024) [373 Item(s)] || lowbit_MC04_stage3_GMAO_relative_humidity_2048x1024_en.mp4 (2048x1024) [3.7 MB] ||
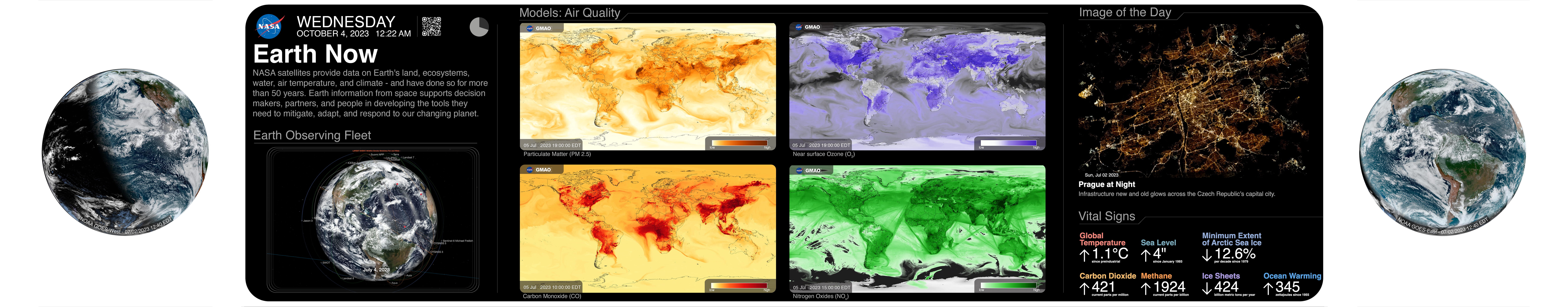
Models: Air Quality
Predictions of air pollution are created using complex models that combine information about weather and the emissions, transformation, and transport of chemical species and particles. The Goddard Earth Observing System Composition Forecasting (GEOS-CF) system is a research model maintained by NASA’s Global Modeling and Assimilation Office to help scientists understand the causes and impact of air pollution. It is one of the highest resolution and most detailed models of its kind in the world, made possible through ongoing collaborations between NASA and university scientists. GEOS-CF tracks the concentrations of hundreds of gas phase chemical species and dozens of types of particles characterized by their composition and size. It is used by a wide variety of stakeholders around the world to develop new methods for improving local predictions, understanding the impact of pollution on human health, and improving the quality of NASA satellite datasets.
Particulate Matter (PM) 2.5
Go to this pageNear surface concentration of fine particular matter (PM2.5) estimated from NASA’s aerosol and weather fields produced by NASA’s GEOS-CF model. || MC01_stage4_GMAO_pm25_2048x1024_en.00001_print.jpg (1024x512) [197.2 KB] || ParticulateMatter_GMAO.png (560x227) [3.5 KB] || MC01_stage4_GMAO_pm25_2048x1024_en.00001_searchweb.png (320x180) [98.9 KB] || MC01_stage4_GMAO_pm25_2048x1024_en.00001_thm.png (80x40) [6.9 KB] || MC01_stage4_GMAO_pm25_2048x1024_en.mp4 (2048x1024) [19.1 MB] || MC01_stage4_GMAO_pm25_2048x1024_en-hwtool (2048x1024) [373 Item(s)] || lowbit_MC01_stage4_GMAO_pm25_2048x1024_en.mp4 (2048x1024) [3.7 MB] ||
Near surface Ozone (O3)
Go to this pageNear surface concentration of ozone (O3) estimated by NASA’s GEOS-CF model. || MC02_stage4_GMAO_O3_2048x1024_en.00001_print.jpg (1024x512) [146.9 KB] || Ozone_GMAO.png (560x227) [3.6 KB] || MC02_stage4_GMAO_O3_2048x1024_en.00001_searchweb.png (320x180) [97.0 KB] || MC02_stage4_GMAO_O3_2048x1024_en.00001_thm.png (80x40) [7.1 KB] || MC02_stage4_GMAO_O3_2048x1024_en.mp4 (2048x1024) [22.6 MB] || MC02_stage4_GMAO_O3_2048x1024_en-hwtool (2048x1024) [373 Item(s)] || lowbit_MC02_stage4_GMAO_O3_2048x1024_en.mp4 (2048x1024) [3.7 MB] ||
Carbon Monoxide (CO)
Go to this pageNear surface concentration of carbon monoxide (CO) estimated by NASA’s GEOS-CF model. || MC03_stage4_GMAO_CO_2048x1024_en.00001_print.jpg (1024x512) [180.4 KB] || CarbonMonoxide_GMAO.png (560x227) [3.5 KB] || MC03_stage4_GMAO_CO_2048x1024_en.00001_searchweb.png (320x180) [84.3 KB] || MC03_stage4_GMAO_CO_2048x1024_en.00001_thm.png (80x40) [6.3 KB] || MC03_stage4_GMAO_CO_2048x1024_en.mp4 (2048x1024) [17.7 MB] || MC03_stage4_GMAO_CO_2048x1024_en-hwtool (2048x1024) [373 Item(s)] || lowbit_MC03_stage4_GMAO_CO_2048x1024_en.mp4 (2048x1024) [3.7 MB] ||
Nitrogen Oxides (NOx)
Go to this pageNear surface concentration of Nitrogen Oxides (NOx) estimated from concentrations of nitrogen oxide and nitrogen dioxide produced by sNASA’s GEOS-CF model. || MC04_stage4_GMAO_NO2_2048x1024_en.00001_print.jpg (1024x512) [216.7 KB] || NitrousOxides_GMAO.png (560x227) [3.5 KB] || MC04_stage4_GMAO_NO2_2048x1024_en.00001_searchweb.png (320x180) [106.5 KB] || MC04_stage4_GMAO_NO2_2048x1024_en.00001_thm.png (80x40) [7.7 KB] || MC04_stage4_GMAO_NO2_2048x1024_en.mp4 (2048x1024) [31.5 MB] || MC04_stage4_GMAO_NO2_2048x1024_en-hwtool (2048x1024) [373 Item(s)] || lowbit_MC04_stage4_GMAO_NO2_2048x1024_en.mp4 (2048x1024) [3.7 MB] ||
Visualizations
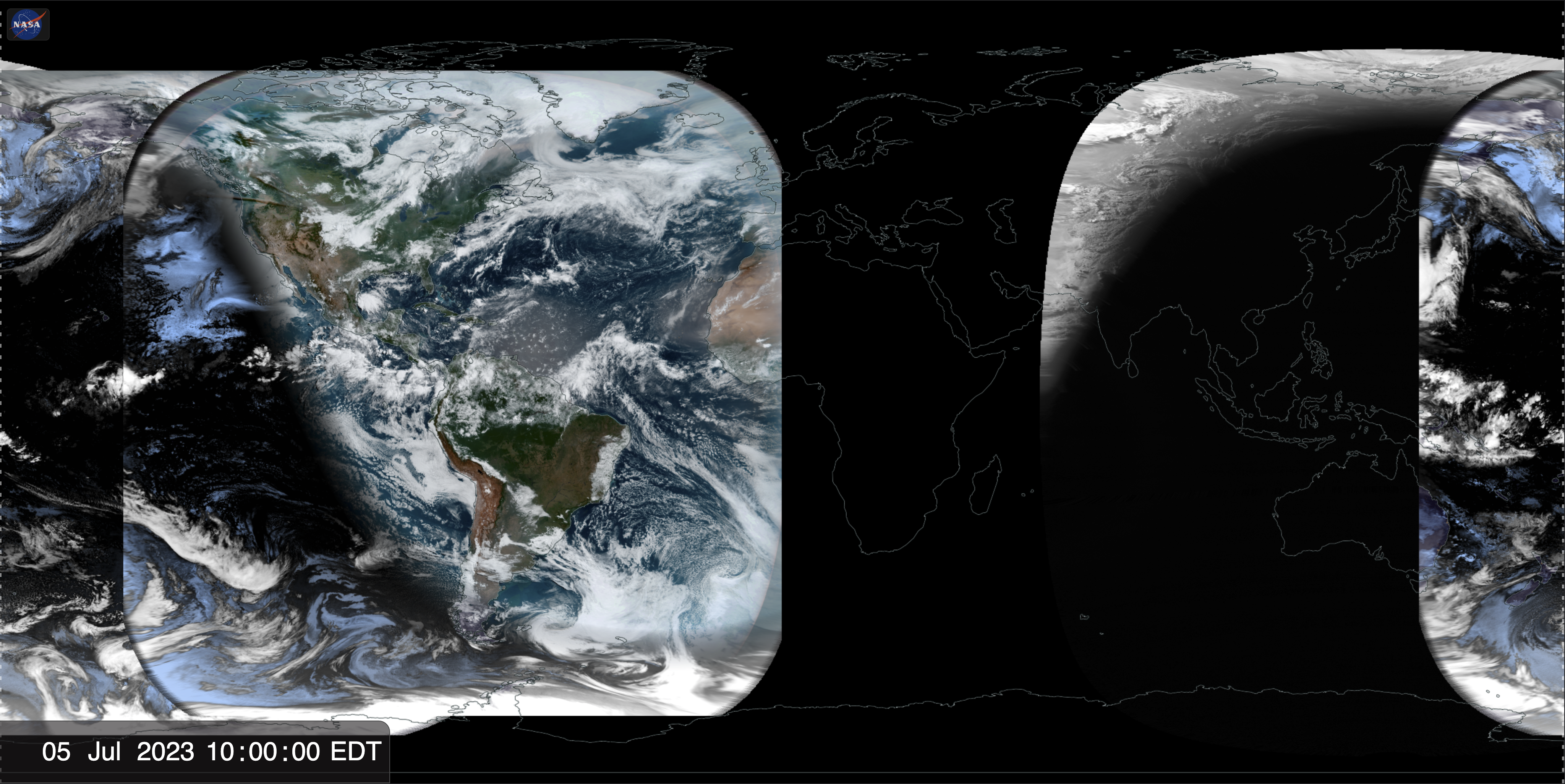
NOAA GOES-East and NOAA GOES-West True Color Imagery Over Past 5 Days
Go to this pageA true color view of the Earth from GOES-16 (GOES-East) over the past 5 days. || PR_WorldView_geostationary_east_2160x2160_en.00001_print.jpg (1024x1024) [306.7 KB] || PR_WorldView_geostationary_east_2160x2160_en.00001_searchweb.png (320x180) [105.7 KB] || PR_WorldView_geostationary_east_2160x2160_en.00001_thm.png (80x40) [7.5 KB] || east (2160x2160) [0 Item(s)] || PR_WorldView_geostationary_east_2160x2160_en.mp4 (2160x2160) [1.1 GB] ||