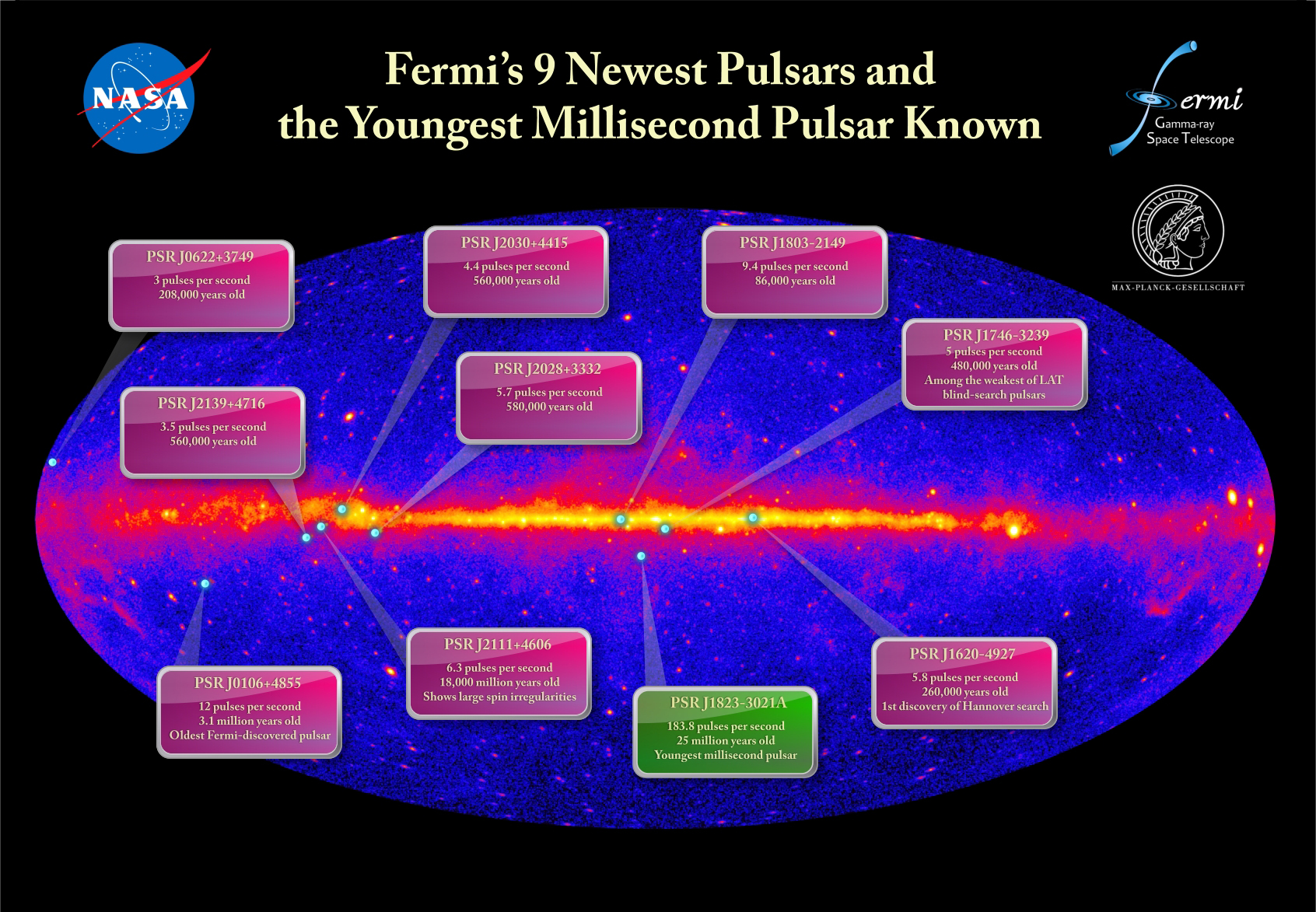
Pulsars Emit Gamma-rays from Equator
A pulsar is a rapidly spinning and highly magnetized neutron star, the crushed core left behind when a massive sun explodes. Most were found through their pulses at radio wavelengths, which are thought to be caused by narrow, lighthouse-like beams emanating from the star's magnetic poles.
When it comes to gamma-rays, pulsars are no longer lighthouses. A new class of gamma-ray-only pulsars shows that the gamma rays must form in a broader region than the lighthouse-like radio beam. Astronomers now believe the pulsed gamma rays arise far above the neutron star.
The pulsar's radio beams (green) never intersect Earth, but its pulsed gamma rays (magenta) do.
Credits
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA/Fermi/Cruz deWilde
-
Animator
- Cruz deWilde (Avant Gravity)
-
Producer
- Stefanie Misztal (UMBC)
-
Scientist
- Steven Ritz (NASA/GSFC)
Release date
This page was originally published on Friday, January 9, 2009.
This page was last updated on Wednesday, May 3, 2023 at 1:54 PM EDT.
Missions
This page is related to the following missions:Series
This page can be found in the following series:Datasets used
-
[Fermi: LAT]
ID: 216Fermi Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope (GLAST) Large Area Telescope (LAT)
This dataset can be found at: http://fermi.gsfc.nasa.gov
See all pages that use this dataset
Note: While we identify the data sets used on this page, we do not store any further details, nor the data sets themselves on our site.