IBEX: Observing the Sun's Horizon
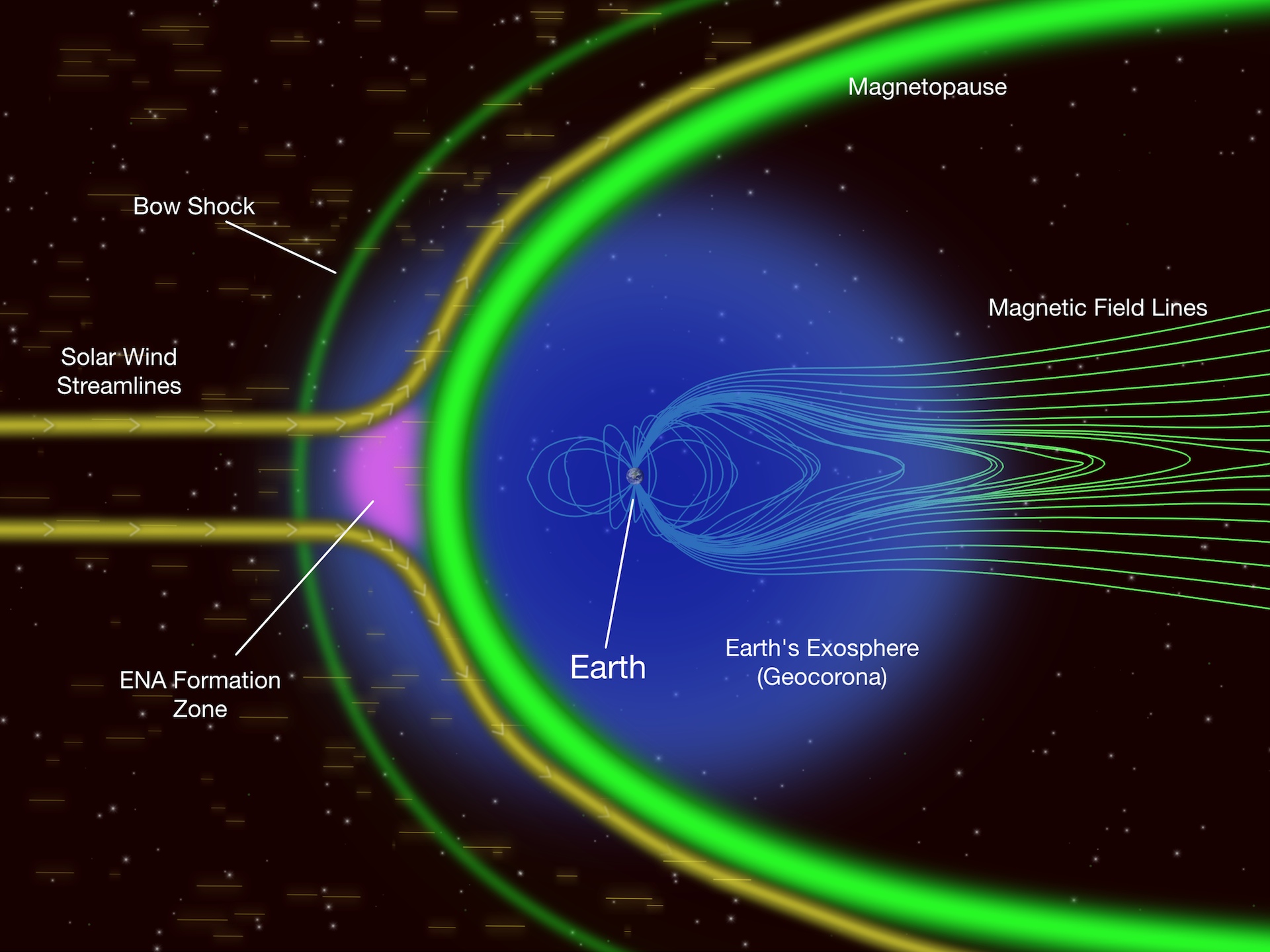
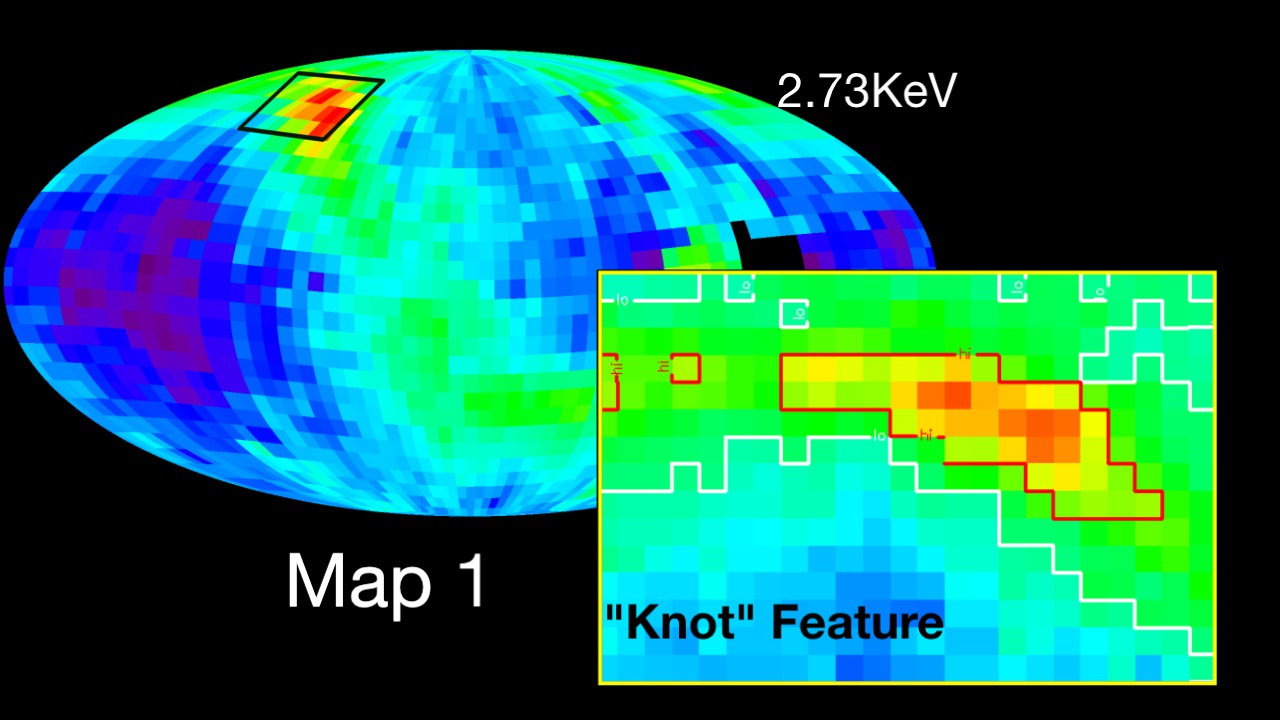
The Interstellar Boundary Explorer, or IBEX, is the first mission designed to map the entire region of the boundary of our Solar System. As charged particles from the Sun, called the "solar wind," flow outward well beyond the orbits of the planets, they collide with the material between the stars, called the "interstellar medium" (ISM). These interactions create energetic neutral atoms (ENAs), particles with no charge that move very quickly. This region emits no light that can be collected by conventional telescopes so, instead, IBEX measures the particles that happen to be traveling inward from the boundary. IBEX contains two detectors designed to collect and measure ENAs, providing data about the mass, location, direction of origin, and energy of these particles. From these data, maps of the boundary are created. IBEX's sole, focused science objective is to discover the nature of the interactions between the solar wind and the interstellar medium at the edge of our Solar System.
Short narrated video about the Interstellar Boundary Explorer spacecraft and mission.
For complete transcript, click here.
Credits
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center
-
Animators
- Walt Feimer (HTSI)
- Tom Bridgman (Global Science and Technology, Inc.)
- Scott Wiessinger (USRA)
-
Video editor
- Scott Wiessinger (USRA)
-
Narrator
- Scott Wiessinger (USRA)
-
Producer
- Scott Wiessinger (USRA)
-
Scientists
- Eric Christian (NASA/HQ)
- Dave McComas (SwRI)
-
Writers
- Scott Wiessinger (USRA)
- Karen Fox (ADNET Systems, Inc.)
Release date
This page was originally published on Thursday, May 10, 2012.
This page was last updated on Wednesday, May 3, 2023 at 1:53 PM EDT.
Series
This page can be found in the following series:Tapes
The media on this page originally appeared on the following tapes:-
IBEX ISM Press Conference
(ID: 2012009)
Tuesday, January 31, 2012 at 5:00AM
Produced by - Robert Crippen (NASA)
Datasets used
-
[IBEX]
ID: 207
Note: While we identify the data sets used on this page, we do not store any further details, nor the data sets themselves on our site.
![Watch this video on the NASA Goddard YouTube channel.Music credits: “End of Days - Joe Mason Remix” by Connor Shambrook [BMI], Cyrus Reynolds [BMI], Flynn Hase Spence [ASCAP], Joseph Scott Mason [APRA]; “Brainstorming” by Laurent Dury [SACEM]; “Flight of the Leaf Remix” by Julie Gruss [GEMA], Laurent Dury [SAXEM]; “Ticks and Thoughts” by Laurent Dury [SACEM]; “Intimate Journey” by Laurent Vernerey [SACEM], Nicolas de Ferran [SACEM] from Universal Production MusicComplete transcript available.](/vis/a010000/a013600/a013642/13642_IBEX11years_YouTube.00214_print.jpg)