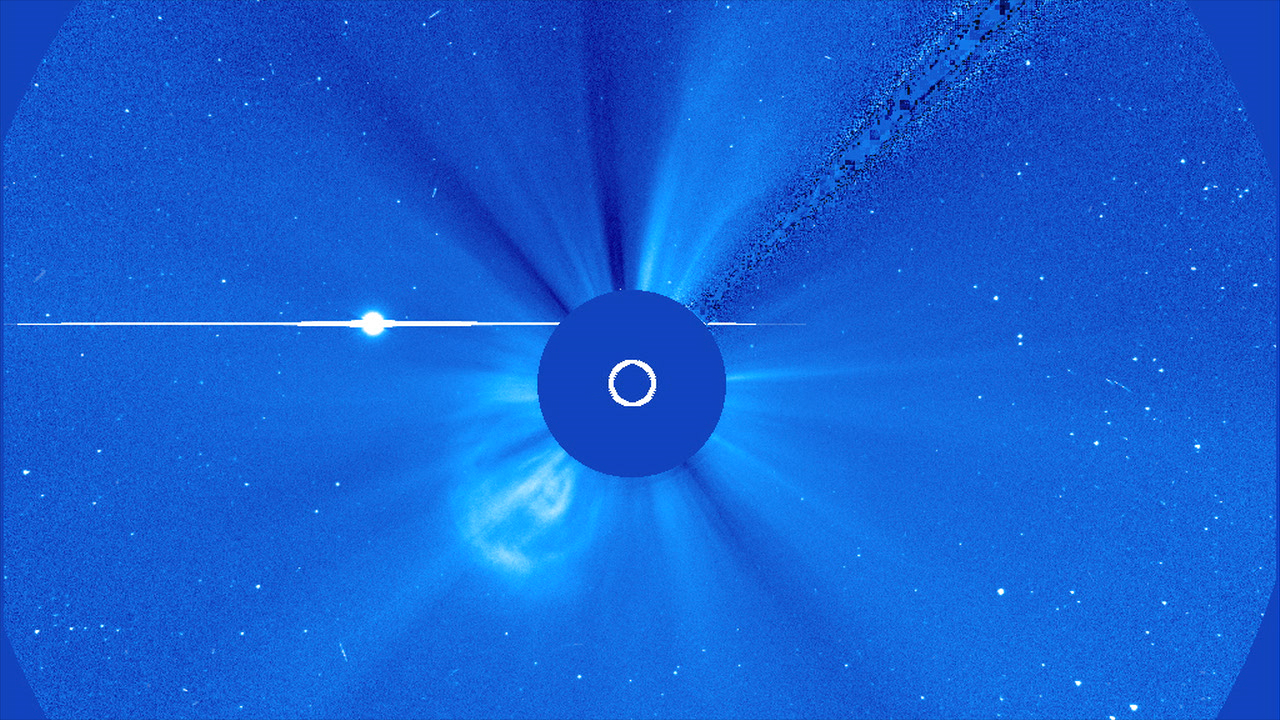
SDO's Ultra-high Definition View of 2012 Venus Transit
Launched on Feb. 11, 2010, the Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO, is the most advanced spacecraft ever designed to study the sun. During its five-year mission, it will examine the sun's atmosphere, magnetic field and also provide a better understanding of the role the sun plays in Earth's atmospheric chemistry and climate. SDO provides images with resolution 8 times better than high-definition television and returns more than a terabyte of data each day.
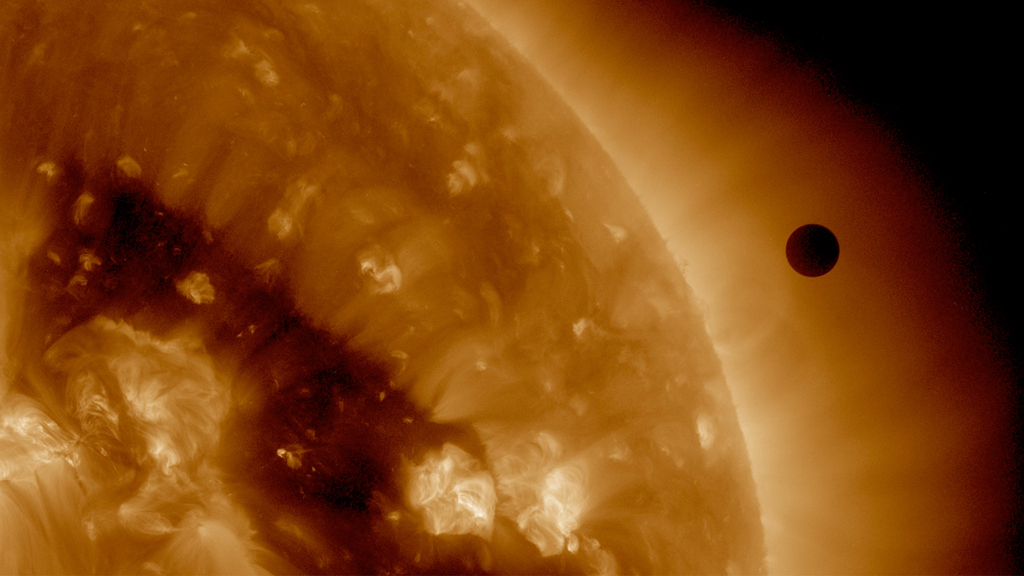
On June 5 2012, SDO collected images of the rarest predictable solar event—the transit of Venus across the face of the sun. This event lasted approximately 6 hours and happens in pairs eight years apart, which are separated from each other by 105 or 121 years. The last transit was in 2004 and the next will not happen until 2117.
The videos and images displayed here are constructed from several wavelengths of extreme ultraviolet light and a portion of the visible spectrum. The red colored sun is the 304 angstrom ultraviolet, the golden colored sun is 171 angstrom, the magenta sun is 1700 angstrom, and the orange sun is filtered visible light. 304 and 171 show the atmosphere of the sun, which does not appear in the visible part of the spectrum.
Collection of SDO footage of transit in multiple wavelengths set to music. The music track is "Dramatic Intro" from Stockmusic.net
For complete transcript, click here.

Sequence of images of 171 transit composited together to show path of Venus. This now has an improved version with better color and detail and a full 4kx4k or cropped 4kx2k size suitable for print.

193 angstrom image from SDO

171 angstrom

HMI Continuum. Portion of visible spectrum. Full size versions and half-size versions.

Cropped HMI Continuum

304 angstrom full disk. In 4k and 2k.

Cropped 304.

171 Mid-transit cropped

171 full disk Mid-transit in 4k and 2k

304 Mid-transit cropped

304 full disk mid-transit 4k and 2k

171 Egress begins. Cropped.

171 Egress begins. Full disk 4k and 2k.

304 Egress begins. Cropped.

304 Egress begins. Full disk 4k and 2k.

HMI Continuum. Almost gone...

193 Showing Venus completely off the limb and backlit by only the corona.
Credits
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center/SDO
-
Animators
- Tom Bridgman (Global Science and Technology, Inc.)
- Scott Wiessinger (USRA)
-
Video editor
- Scott Wiessinger (USRA)
-
Producer
- Scott Wiessinger (USRA)
-
Project support
- Swarupa Nune (Vantage)
Release date
This page was originally published on Tuesday, June 5, 2012.
This page was last updated on Sunday, January 12, 2025 at 12:19 AM EST.
Missions
This page is related to the following missions:Series
This page can be found in the following series:Tapes
The media on this page originally appeared on the following tapes:-
Transit of Venus
(ID: 2012043)
Monday, June 4, 2012 at 4:00AM
Produced by - Robert Crippen (NASA)
Datasets used
-
[SDO]
ID: 168This dataset can be found at: http://sdo.gsfc.nasa.gov/
See all pages that use this dataset -
SDO Continuum (Continuum) [SDO: HMI]
ID: 674 -
AIA 304 (304 Filter) [SDO: AIA]
ID: 677This dataset can be found at: http://jsoc.stanford.edu/
See all pages that use this dataset -
AIA 171 (171 Filter) [SDO: AIA]
ID: 680This dataset can be found at: http://jsoc.stanford.edu/
See all pages that use this dataset
Note: While we identify the data sets used on this page, we do not store any further details, nor the data sets themselves on our site.