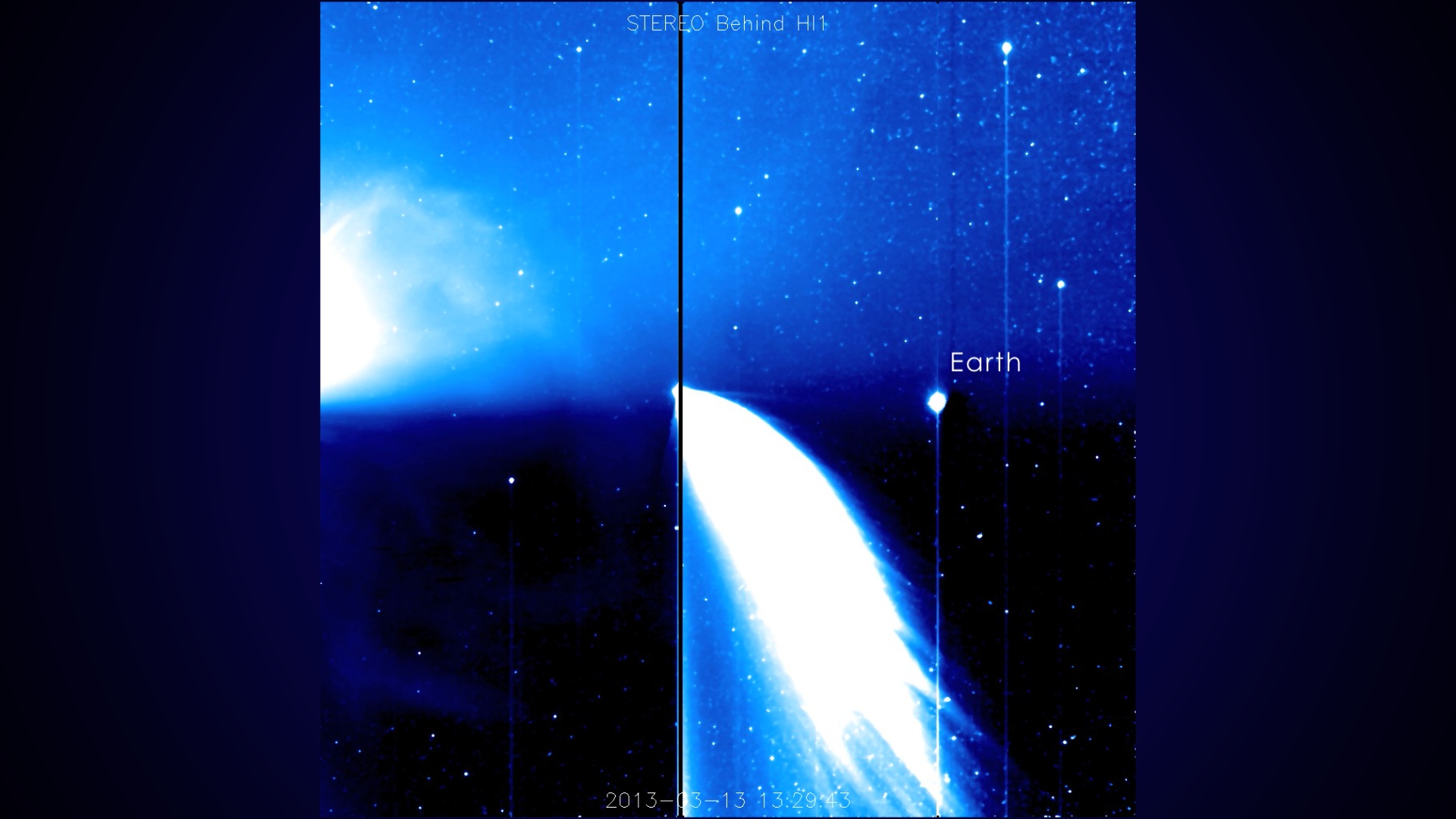
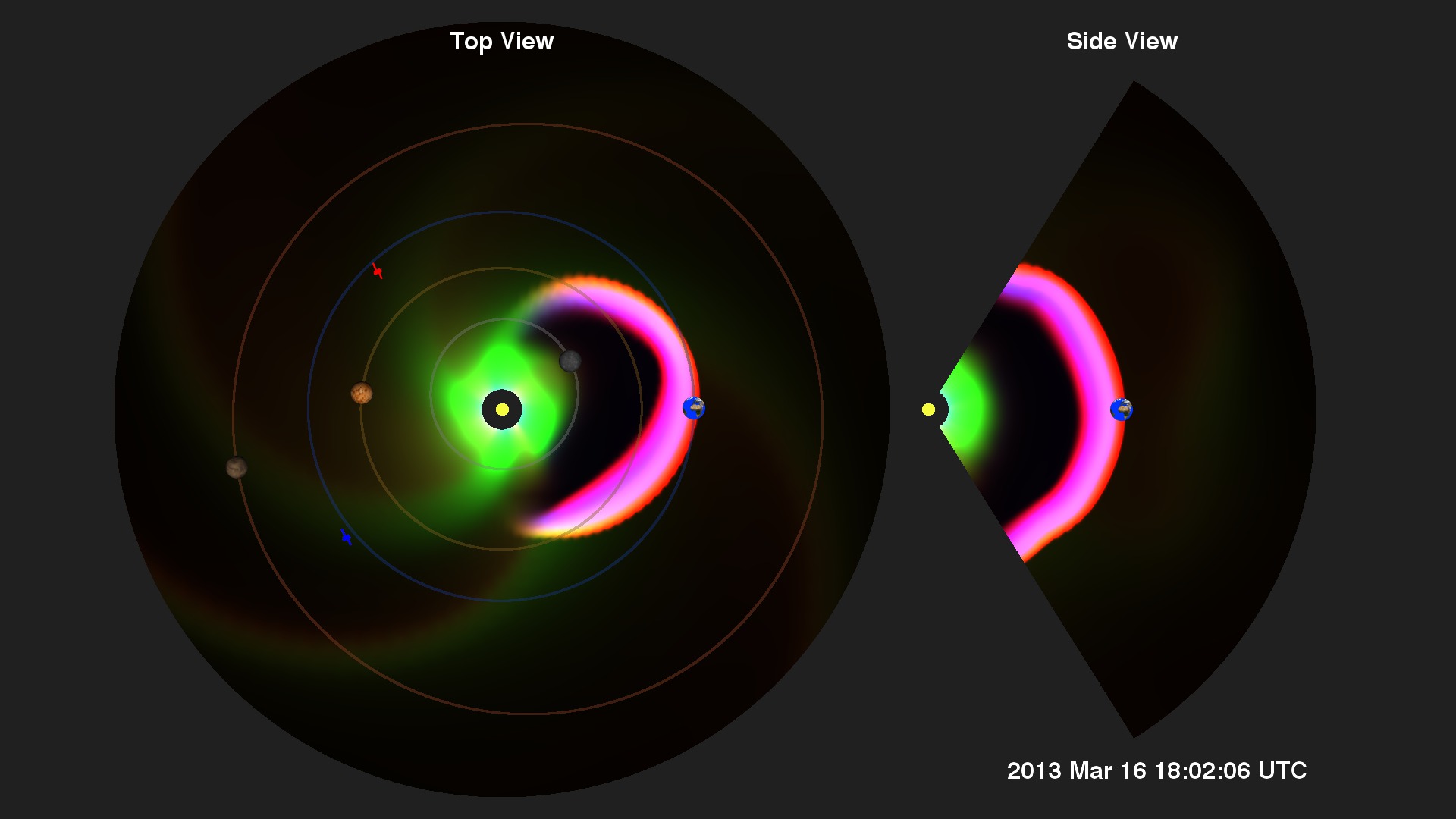
Solar Storm Near Earth Caused by March 15, 2013 Fast CME
On March 15, 2013, at 2:54 a.m. EDT, the sun erupted with an Earth-directed coronal mass ejection (CME), a solar phenomenon that can send billions of tons of solar particles into space and can reach Earth one to three days later and affect electronic systems in satellites and on the ground. Experimental NASA research models, based on observations from the Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory (STEREO) and ESA/NASA's Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, show that the CME left the sun at speeds of around 900 miles per second, which is a fairly fast speed for CMEs. Historically, CMEs at this speed have caused mild to moderate effects at Earth.
Update: On March 17, 2013, at 1:28 a.m. EDT, the coronal mass ejection (CME) from March 15 passed by NASA's Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) as it approached Earth. Upon interacting with the giant magnetic bubble surrounding Earth, the magnetosphere, the CME caused a kind of solar storm known as a geomagnetic storm. The storm initially caused a mild storm rated on NOAA's geomagnetic storm scales as a G2 on a scale from G1 to G5, and subsequently subsided to a G1. In the past, storms of this strength have caused auroras near the poles but have not disrupted electrical systems on Earth or interfered with GPS or satellite-based communications systems.
Model of track of the March 15, 2013 fast moving CME through inner solar system and past Earth. (Note: repeats 4 times)

The ESA and NASA Solar Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) captured these images of the sun spitting out a coronal mass ejection (CME) on March 15, 2013, from 3:24 to 4:00 a.m. EDT. This type of image is known as a coronagraph, since a disk is placed over the sun to better see the dimmer atmosphere around it, called the corona.
Credit: ESA&NASA/SOHO

The ESA and NASA Solar Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) captured these images of the sun spitting out a coronal mass ejection (CME) on March 15, 2013, from 3:24 to 4:00 a.m. EDT. This type of image is known as a coronagraph, since a disk is placed over the sun to better see the dimmer atmosphere around it, called the corona. No Labels
Credit: ESA&NASA/SOHO

SOHO LASCO C2 Coronograph image.

SOHO LASCO C2 Coronograph image.

SOHO LASCO C2 Coronograph image.

SOHO LASCO C2 Coronograph image.

SOHO LASCO C2 Coronograph image.
For More Information
Credits
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
-
Animator
- Tom Bridgman (Global Science and Technology, Inc.)
-
Video editor
- Scott Wiessinger (USRA)
-
Producer
- Scott Wiessinger (USRA)
-
Writer
- Karen Fox (ADNET Systems, Inc.)
Release date
This page was originally published on Monday, March 18, 2013.
This page was last updated on Wednesday, May 3, 2023 at 1:52 PM EDT.
Series
This page can be found in the following series:Tapes
The media on this page originally appeared on the following tapes:-
2013 Heliophysics Breaking News
(ID: 2013021)
Tuesday, December 31, 2013 at 5:00AM
Produced by - Robert Crippen (NASA)