Possible Methane Sources and Sinks on Mars

There are several possible ways that methane can be created, stored, and released on Mars, including both biological and non-biological pathways.
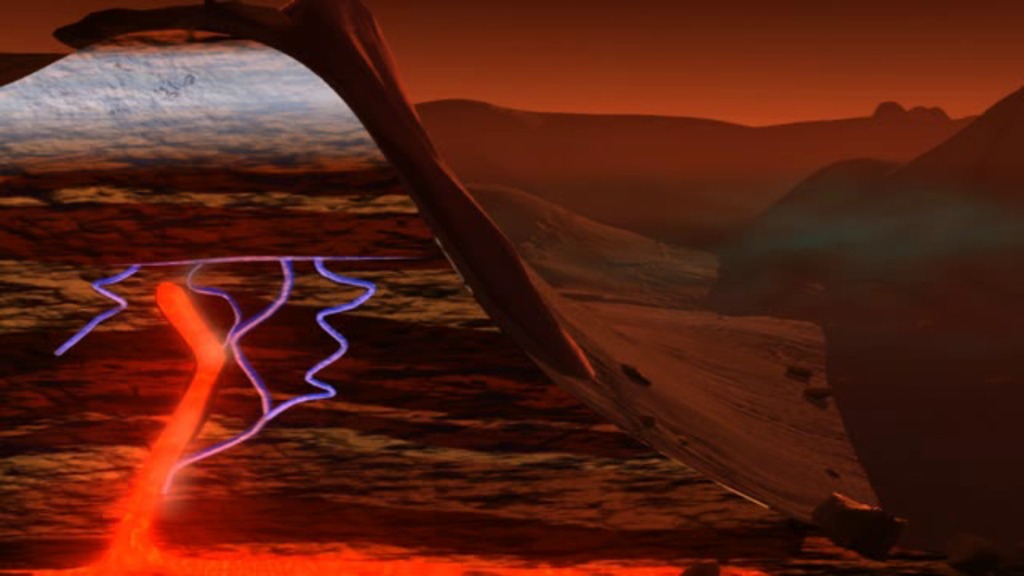
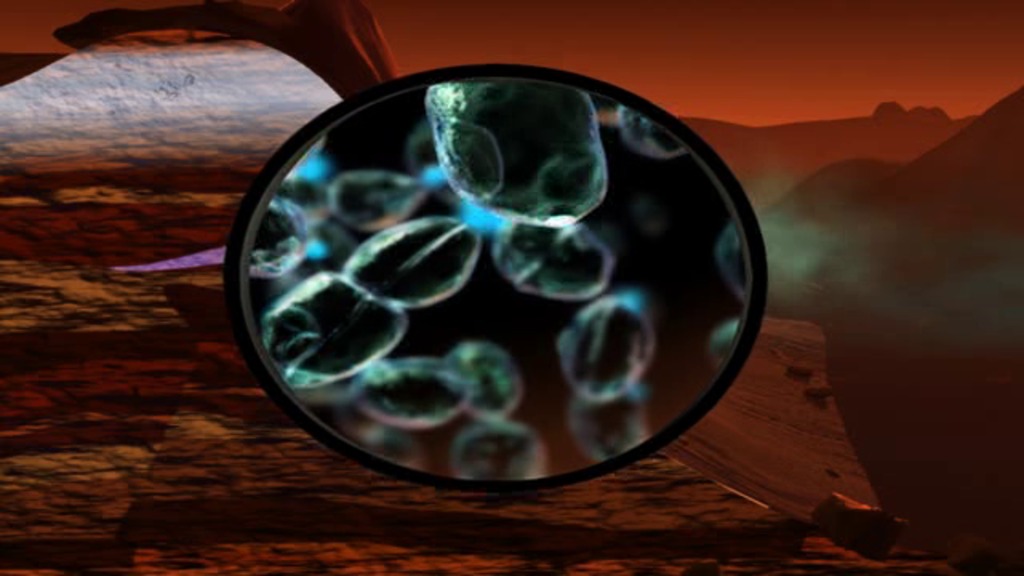
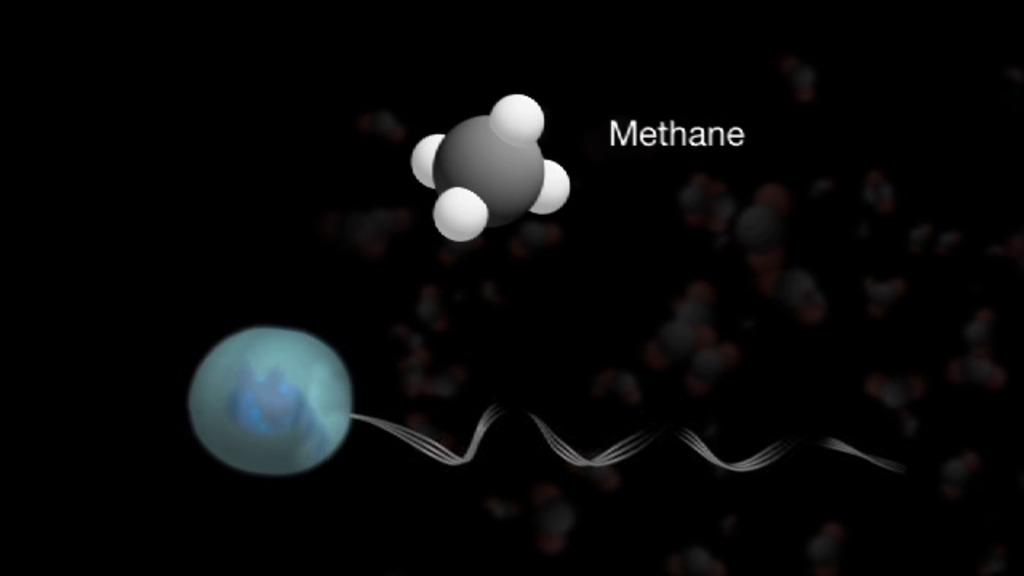
This illustration portrays possible ways that methane might be added to Mars' atmosphere (sources) and removed from the atmosphere (sinks). NASA's Curiosity Mars rover has detected fluctuations in methane concentration in the atmosphere, implying both types of activity occur in the modern environment of Mars.
A molecule of methane consists of one atom of carbon and four atoms of hydrogen. Methane can be generated by microbes and can also be generated by processes that do not require life, such as reactions between water and olivine (or pyroxene) rock. Ultraviolet radiation (UV) can induce reactions that generate methane from other organic chemicals produced by either biological or non-biological processes, such as comet dust falling on Mars. Methane generated underground in the distant or recent past might be stored within lattice-structured methane hydrates called clathrates, and released by the clathrates at a later time, so that methane being released to the atmosphere today might have formed in the past.
Winds on Mars can quickly distribute methane coming from any individual source, reducing localized concentration of methane. Methane can be removed from the atmosphere by sunlight-induced reactions (photochemistry). These reactions can oxidize the methane, through intermediary chemicals such as formaldehyde and methanol, into carbon dioxide, the predominant ingredient in Mars' atmosphere.
Learn more about the detection of methane on Mars.

Graphic with main title only

Graphic without text
For More Information
See NASA.gov
Credits
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
JPL-Caltech
University of Michigan
-
Scientist
- Paul Mahaffy (NASA/GSFC)
-
Graphic designer
- Brian Monroe (USRA)
-
Producer
- David Ladd (USRA)
-
Support
- Dan Gallagher (USRA)
-
Technical support
- Aaron E. Lepsch (ADNET Systems, Inc.)
Release date
This page was originally published on Tuesday, December 16, 2014.
This page was last updated on Wednesday, May 3, 2023 at 1:50 PM EDT.
![Researchers analyzing pulverized rock onboard NASA’s Curiosity rover have found the largest organic compounds on the Red Planet to date.Complete transcript available.Universal Production Music: “Labyrinth of Discovery” by Emma Zarobyan [SOCAN]Watch this video on the NASA Goddard YouTube channel.](/vis/a010000/a014800/a014808/Mars_Large_Organics_Thumbnail_V3.jpg)