NASA Tracks COVID-19’s Atmospheric Fingerprint
Universal Production Music: The Mysterious Staircase by Brice Davoli [SACEM], Suspended in Time by Brice Davoli [SACEM]
Stock Footage: Pond5
Complete transcript available.
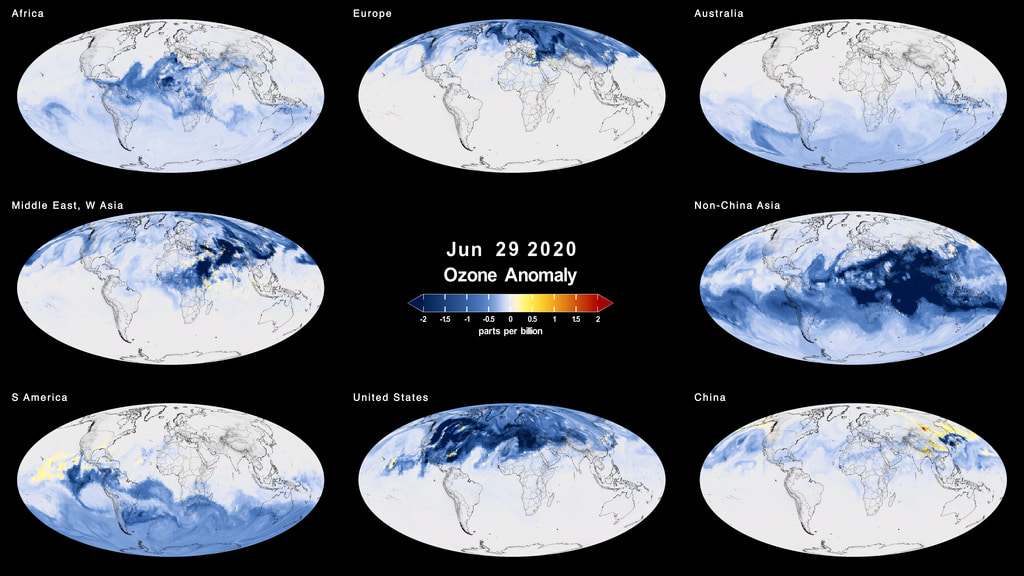
The COVID-19-related lockdowns granted scientists an unexpected and detailed glimpse as to how human activities impact atmospheric composition. Two recent studies, one focusing on nitrogen oxide and the other examining CO2 concentrations, were able to detect the atmospheric ‘fingerprint’ of the lockdowns in unprecedented detail.
Credits
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
-
Scientists
- Kazuyuki Miyazaki (JPL)
- Kevin Bowman (JPL)
- Lesley Ott (NASA/GSFC)
- Brad Weir (Morgan State University)
-
Producer
- Katie Jepson (KBR Wyle Services, LLC)
-
Visualizer
- Trent L. Schindler (USRA)
-
Writers
- Ellen T. Gray (ADNET Systems, Inc.)
- Jessica Merzdorf (Telophase)
-
Narration
- Katie Jepson (KBR Wyle Services, LLC)
Release date
This page was originally published on Thursday, March 24, 2022.
This page was last updated on Wednesday, May 3, 2023 at 11:44 AM EDT.