A newer version of this visualization is available.
Oceanic Niño Index through May 2018
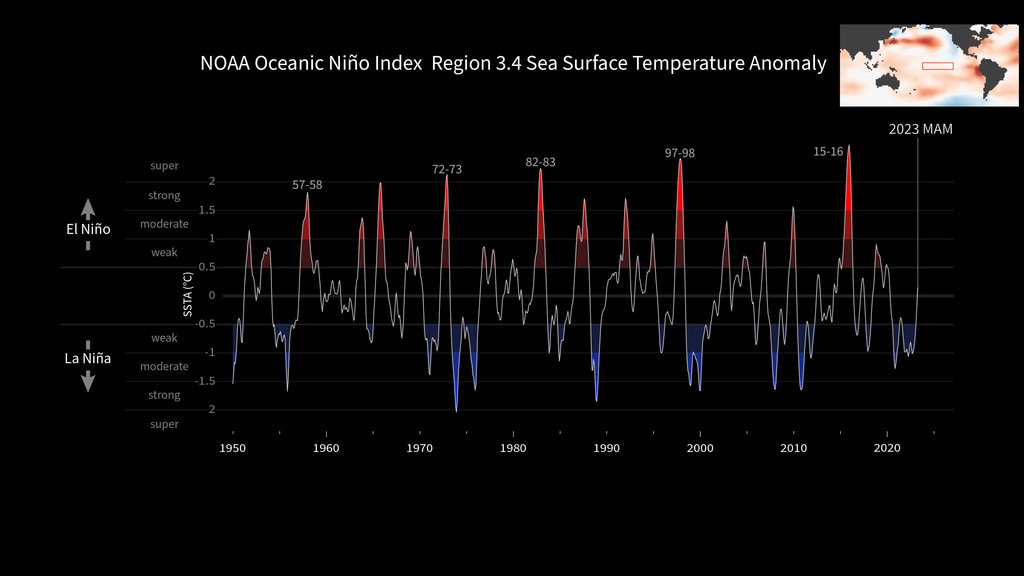
Animated plot of the Oceanic Niño Index (ONI) from 1950-2018
The Oceanic Niño Index (ONI) is is NOAA's primary indicator for monitoring El Niño and La Niña, which are opposite phases of the climate pattern called the El Niño-Southern Oscillation, or “ENSO” for short.
The ONI is the difference between a three month running average of the sea surface temperature averaged over an area of the ocean from 120 West to 170 West longitude along the equator and the long term average for the same three months.
NOAA considers El Niño conditions to be present when the Oceanic Niño Index is +0.5 or higher, indicating the east-central tropical Pacific is significanty warmer than usual. La Niña conditions exist when the Oceanic Niño Index is -0.5 or lower, indicating the region is cooler than usual.
For More Information
Credits
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA
-
Visualizer
Release date
This page was originally published on Wednesday, July 18, 2018.
This page was last updated on Monday, January 6, 2025 at 2:57 AM EST.