The Active Sun from SDO: EUV Variability Experiment (EVE)
The Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) observes the Sun with many different instruments, in many different wavelengths of light. Many of these capabilities are not possible for ground-based observatories - hence the need for a space-based observing platform.
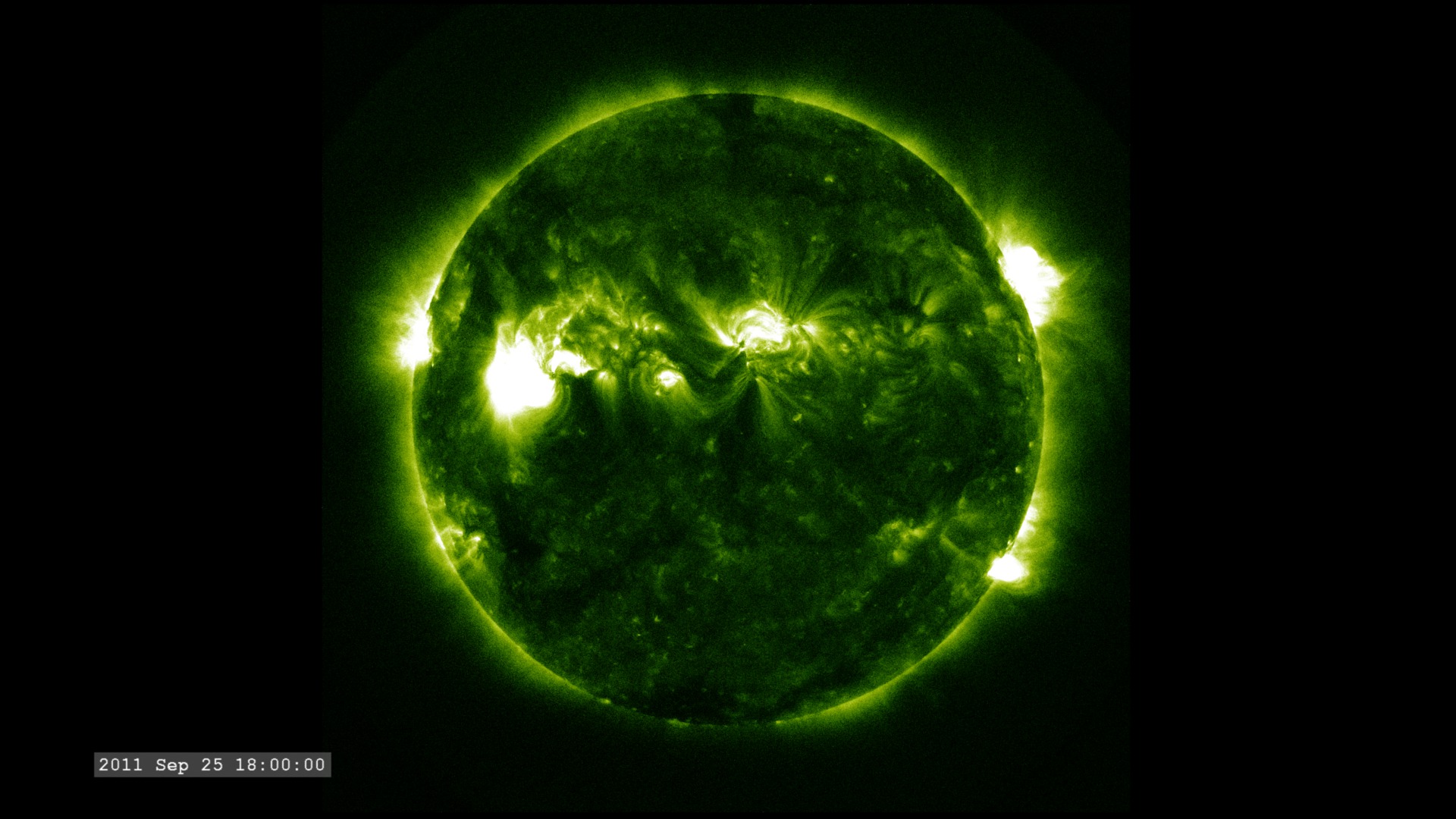
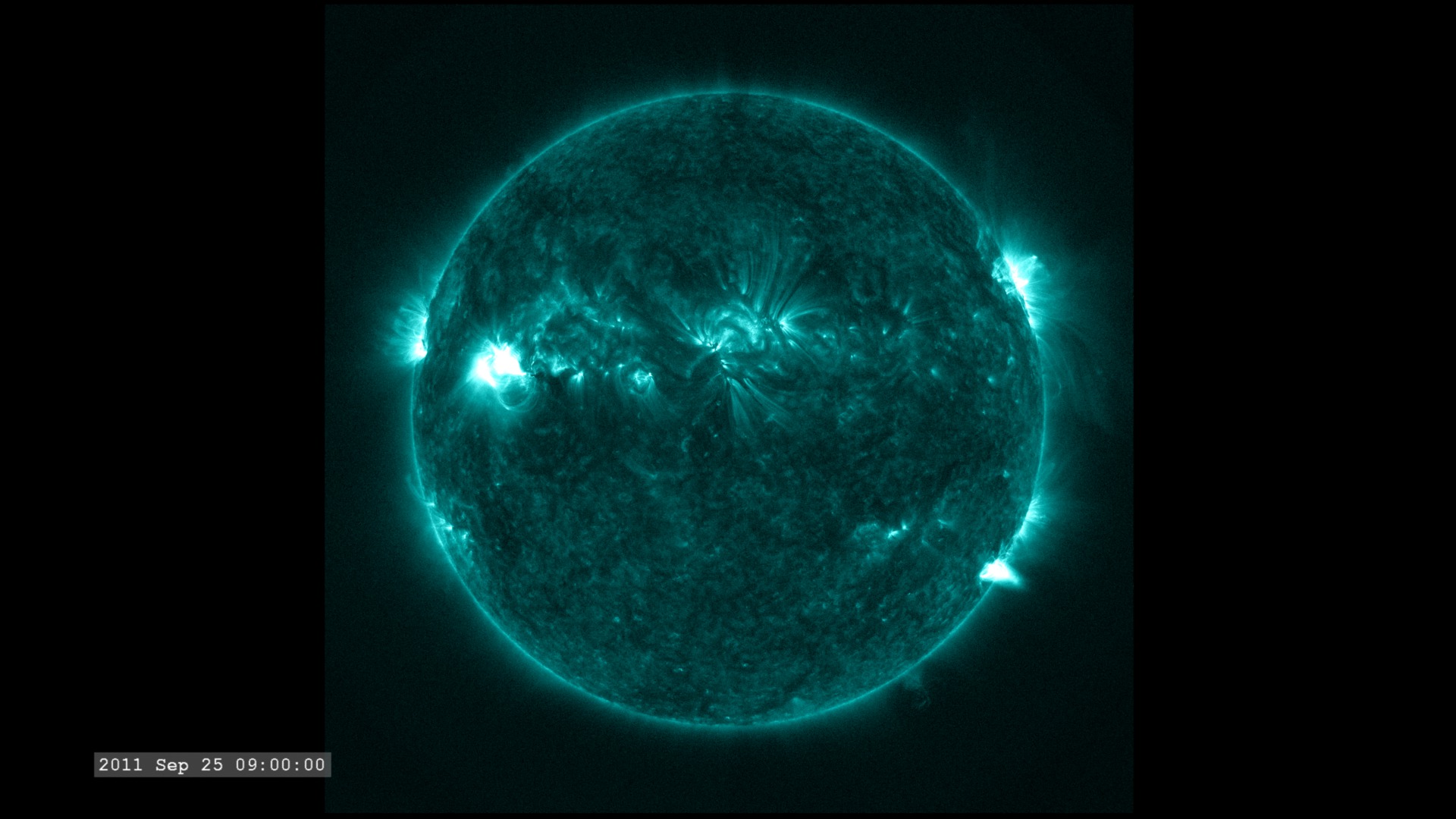
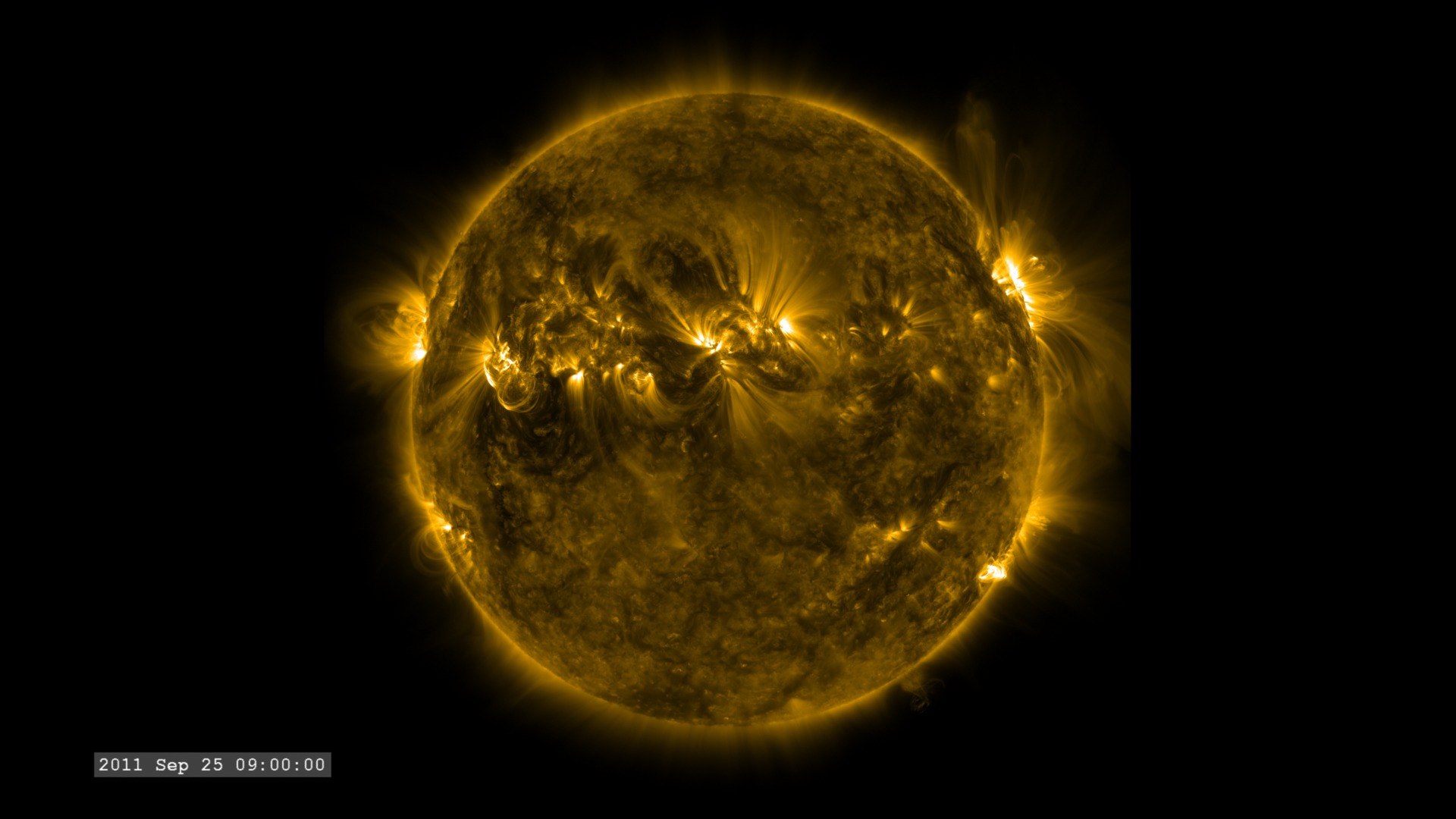
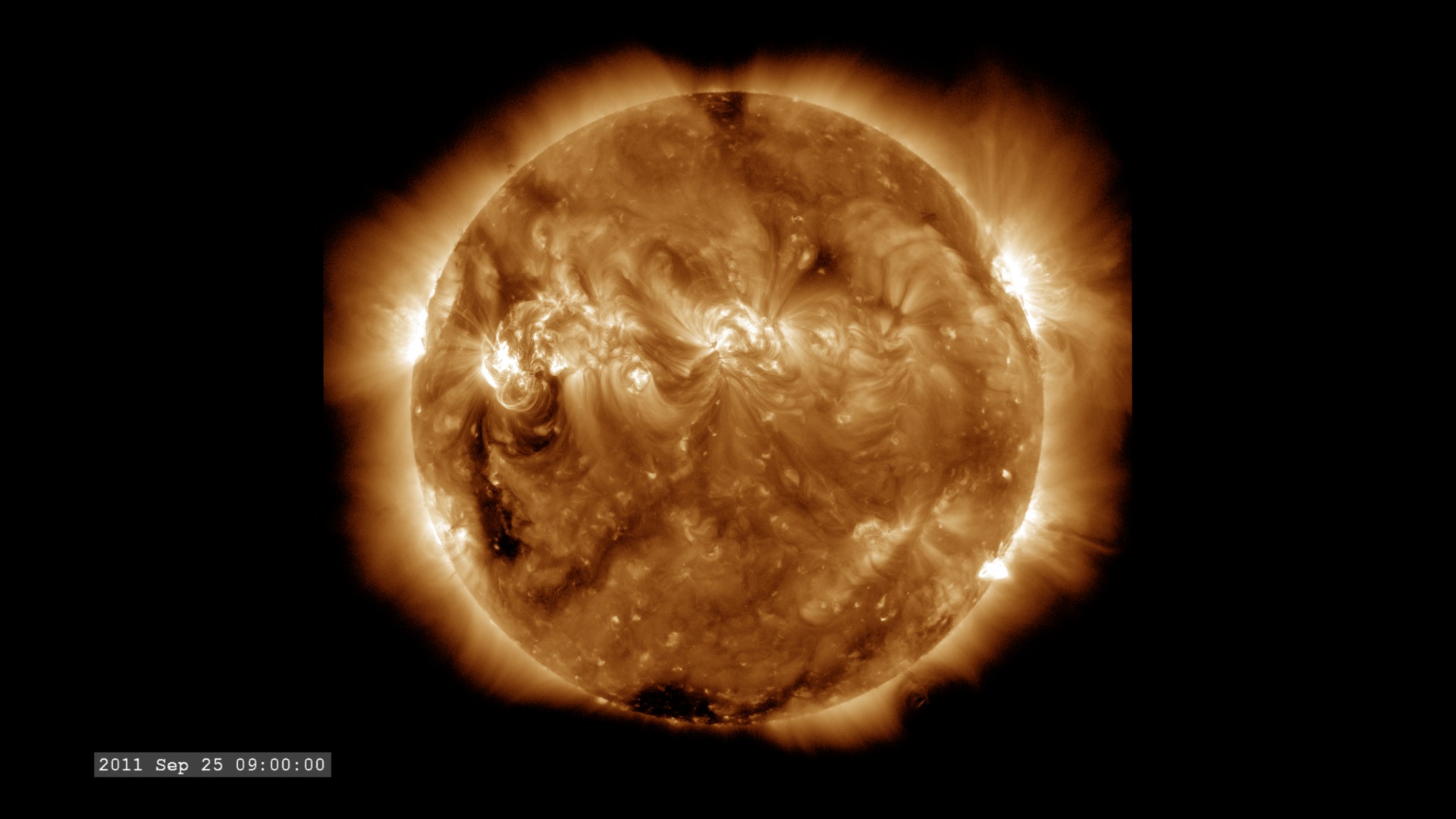
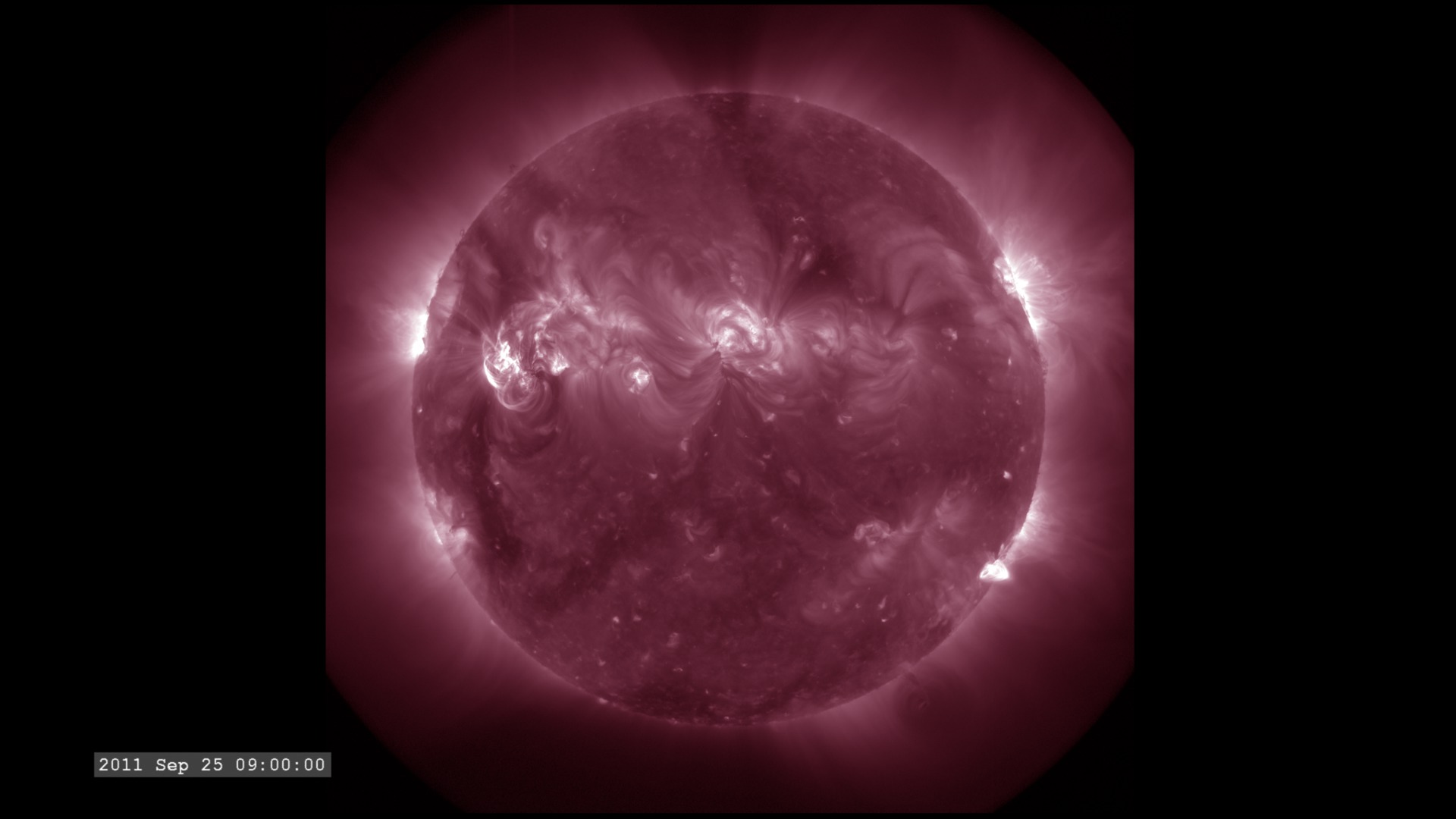
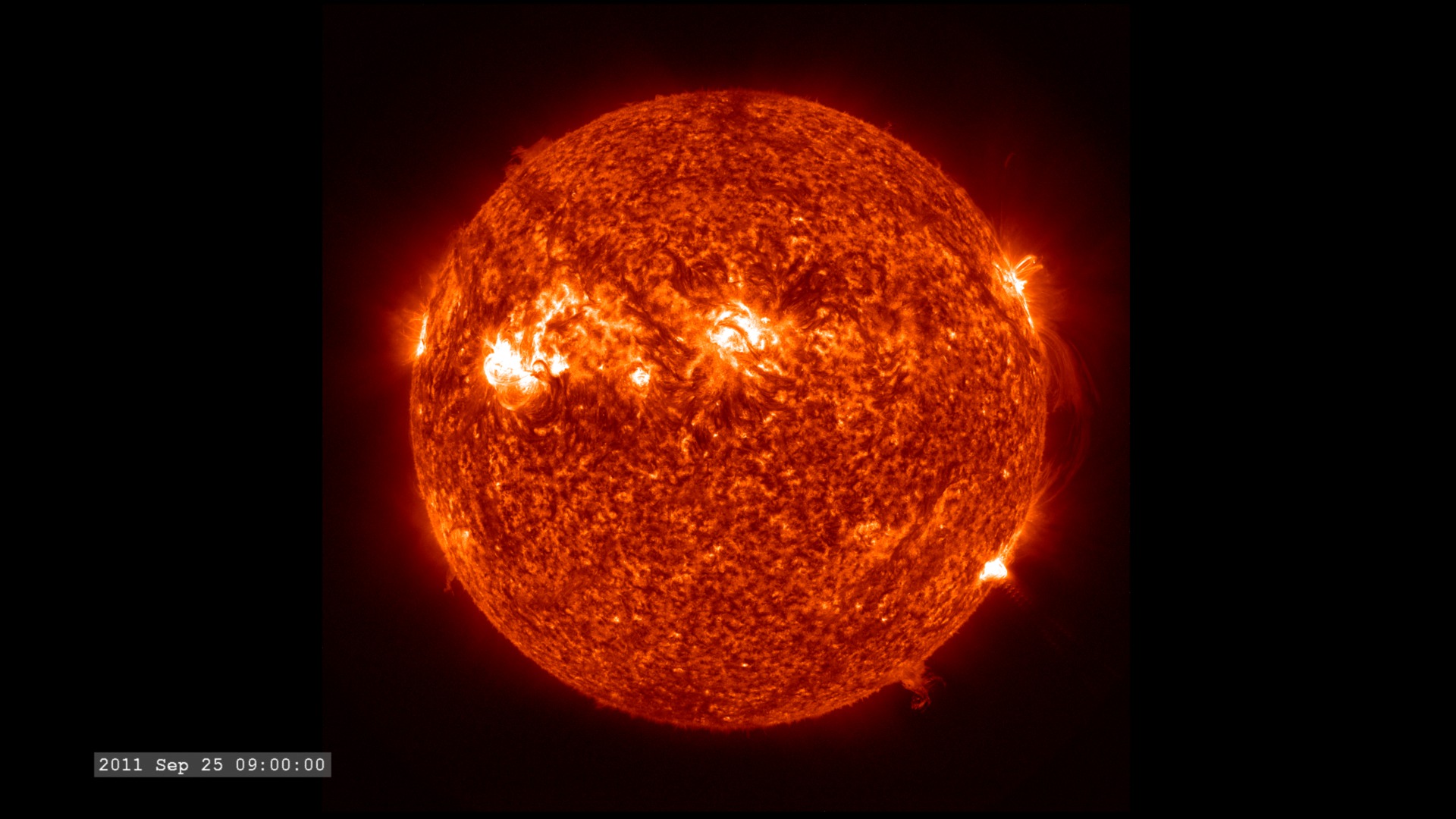
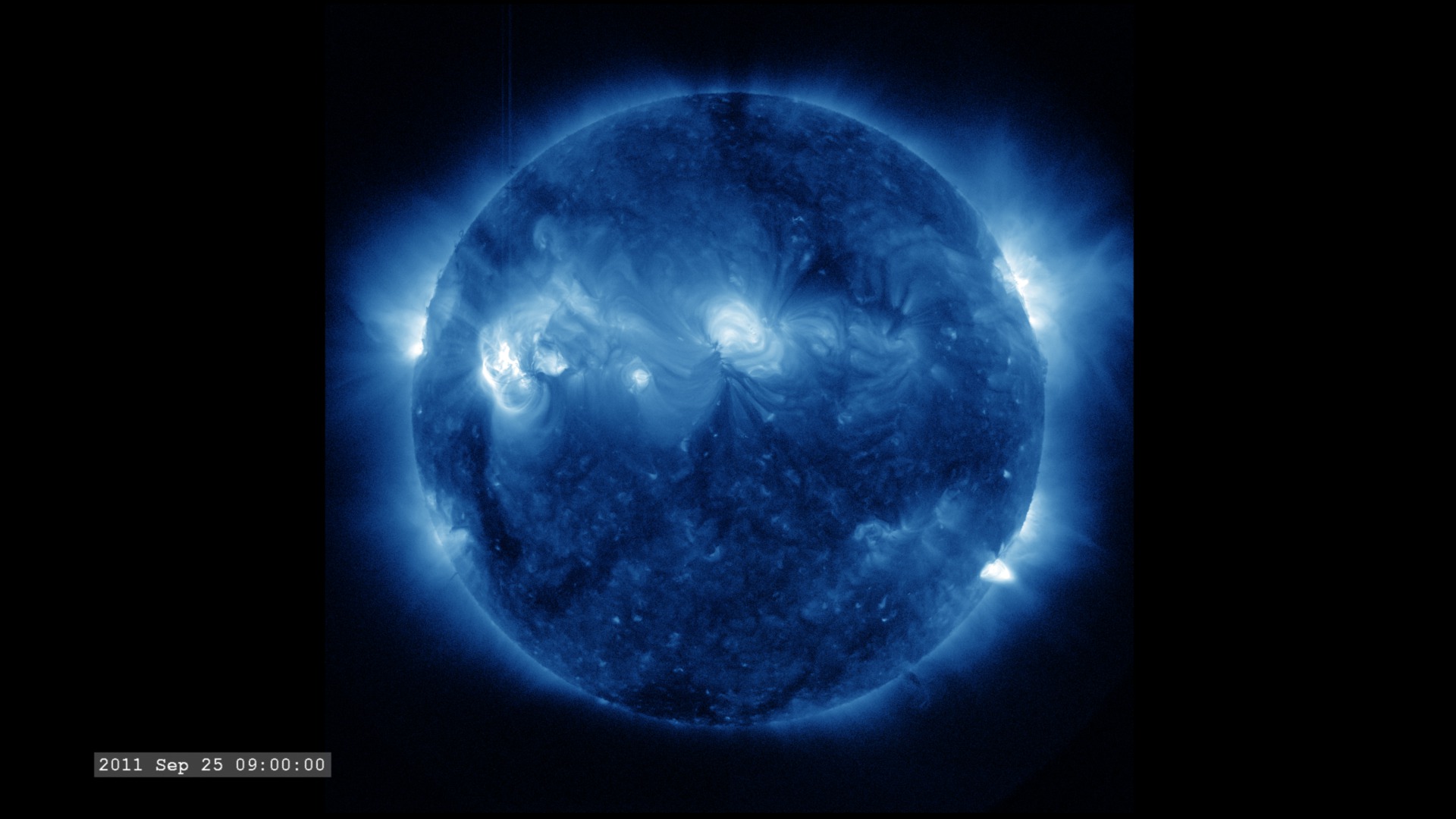
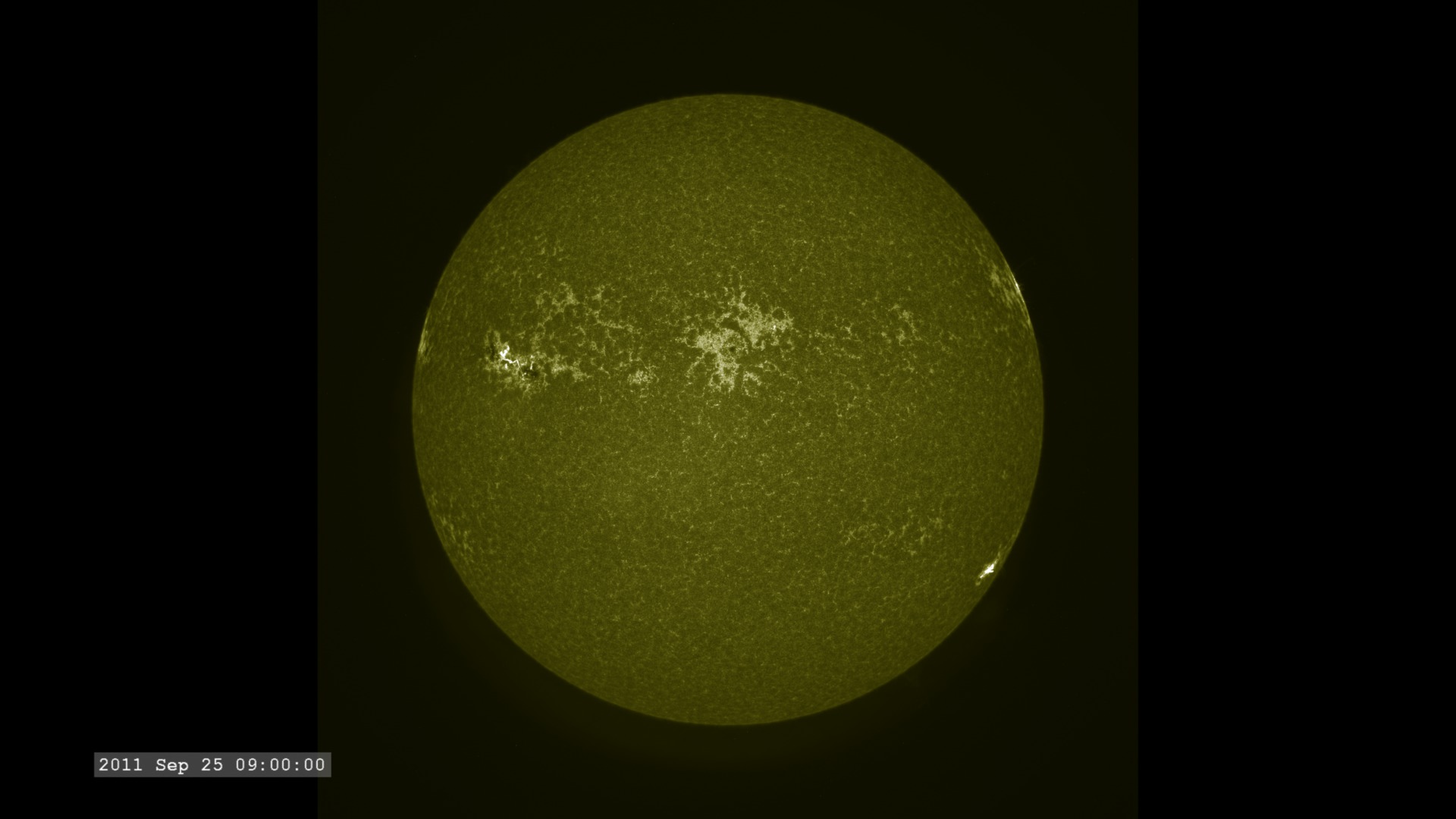
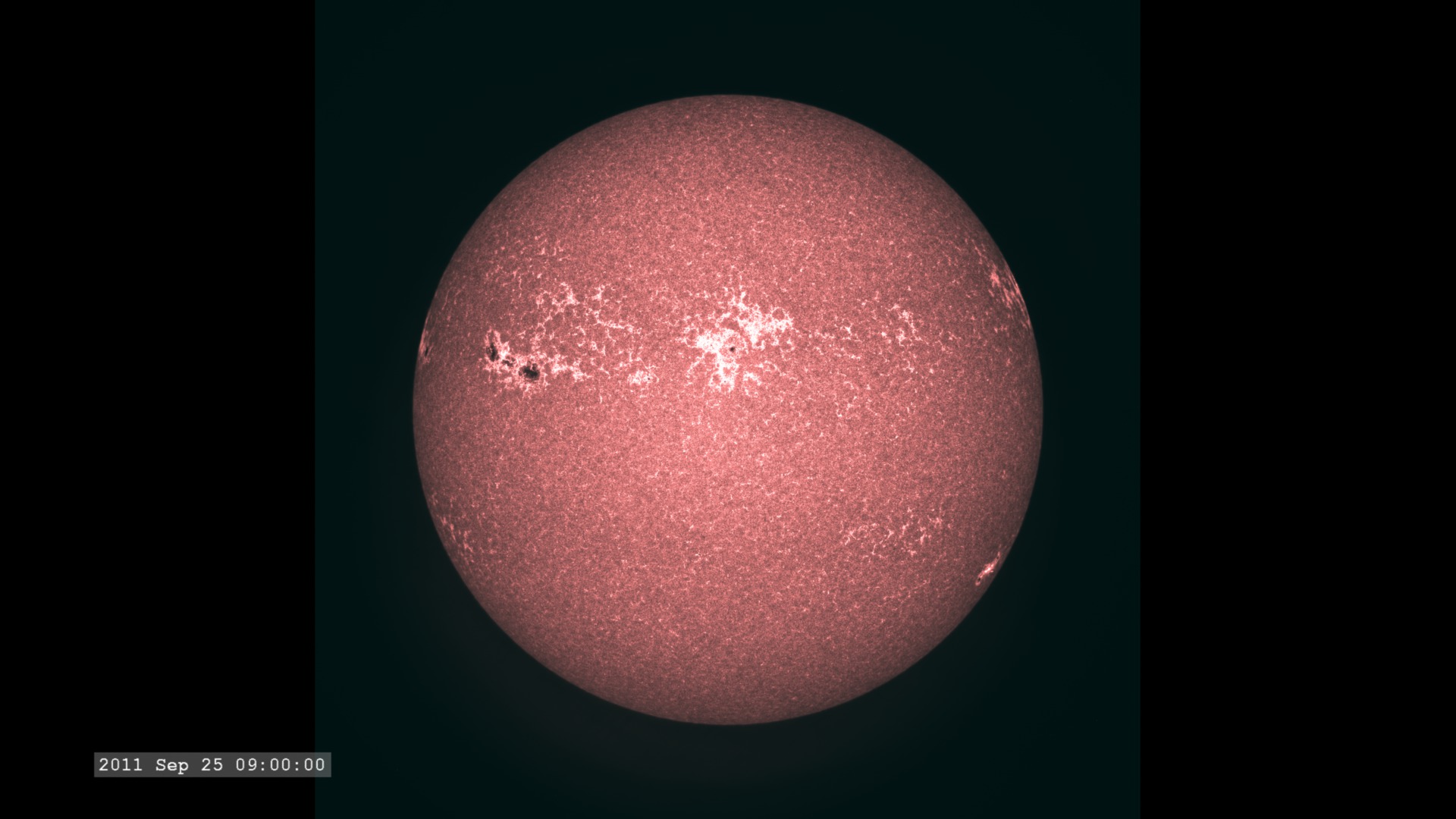
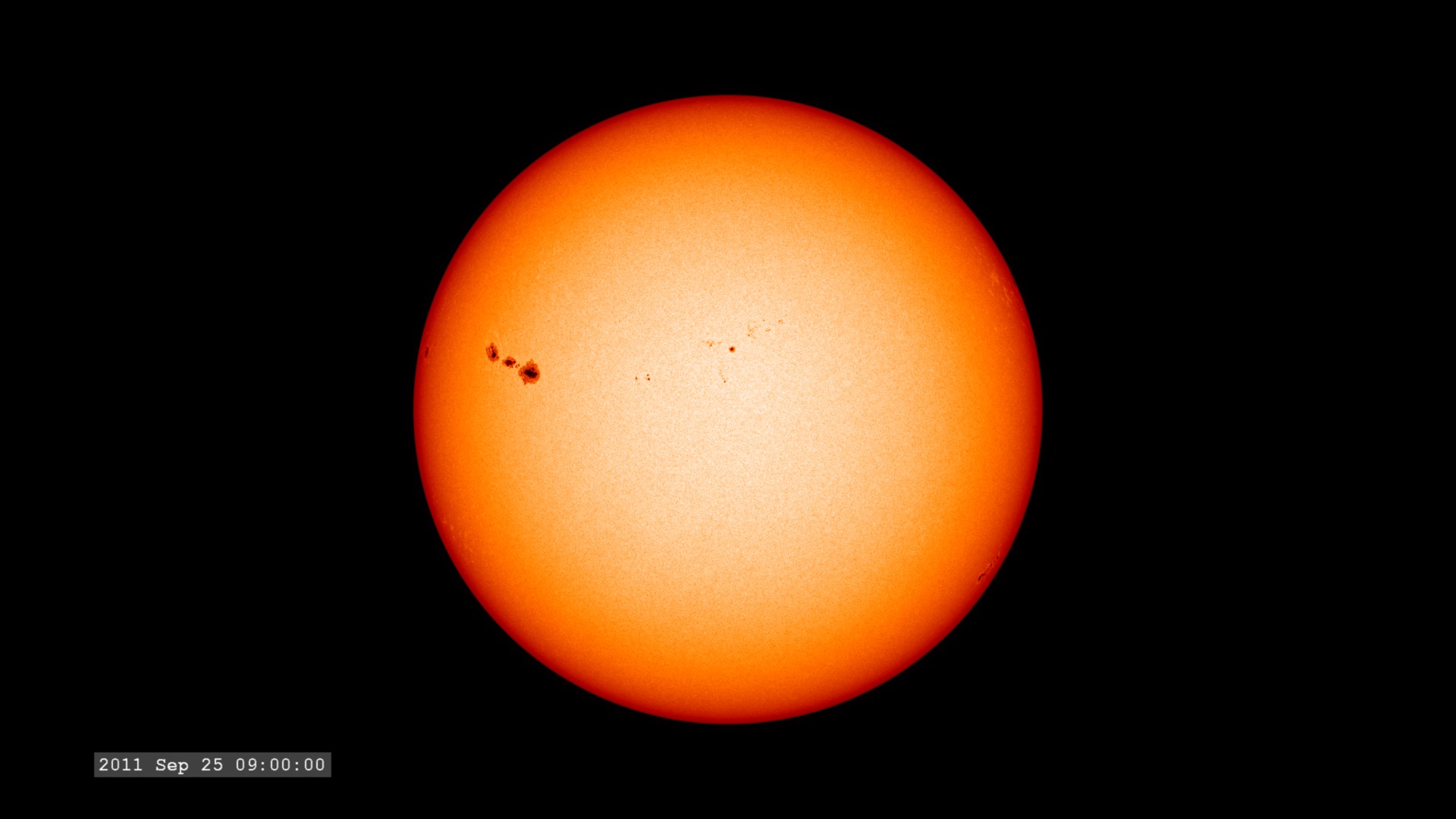
The Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) Variability Experiment (EVE) measures extreme ultraviolet emission from the solar chromosphere, transition region and corona. This radiation is mostly absorbed in Earth's upper atmosphere and influences Earth's climate.
This visualization is one of a set of visualizations (others linked below) covering the same time span of 17 hours over the full wavelength range of the mission. They are setup to play synchronously on a Hyperwall, or can be run individually.
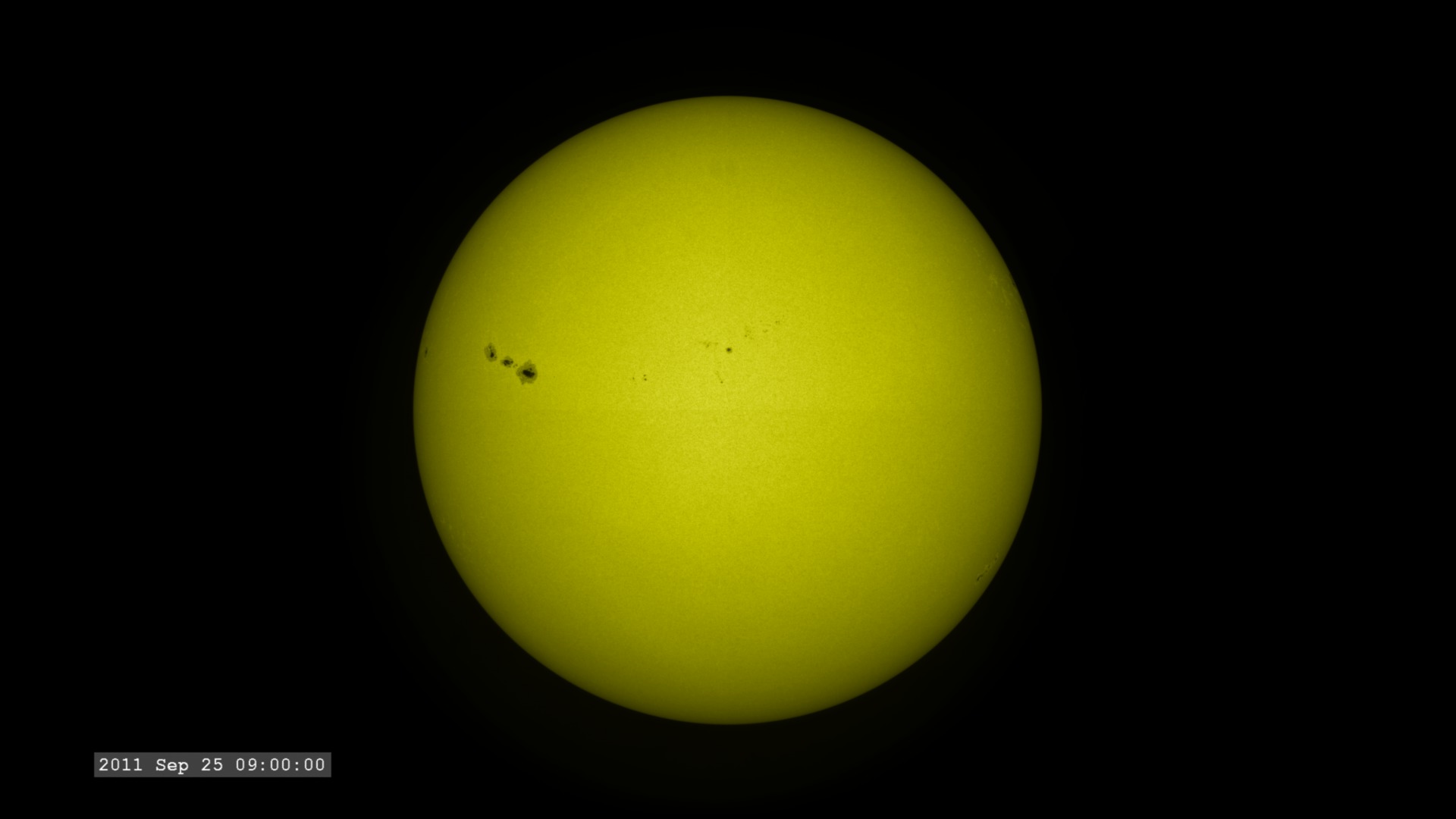
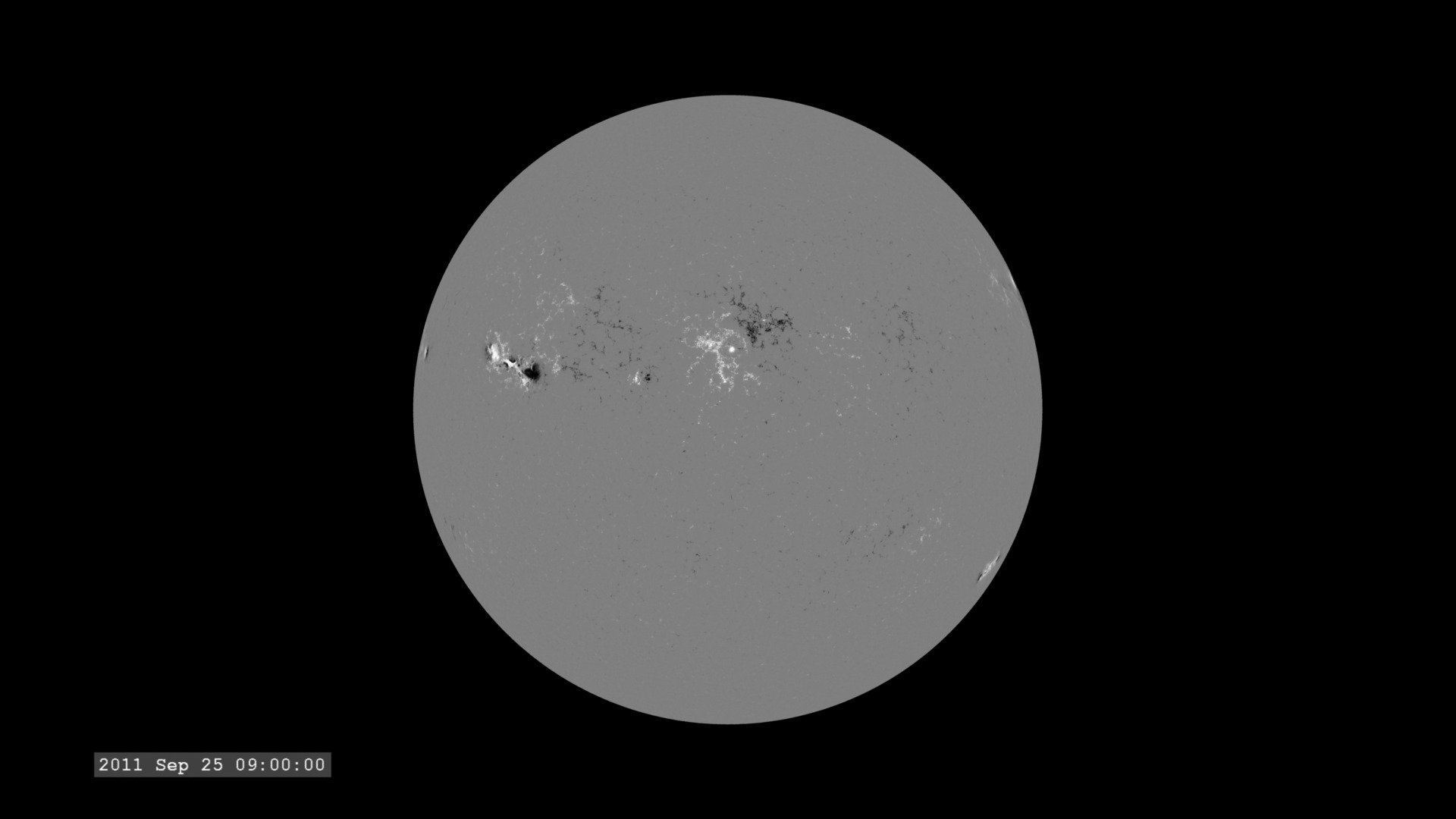
The images are sampled every 36 seconds, 1/3 of the standard time-cadence for SDO. This visualization is useful for illustrating how different solar phenomena, such as sunspots and active regions, look very different in different wavelengths of light. This differences enable scientists to study them more completely, with an eventual goal of improving Space Weather forecasting.
A plot of EVE spectral data with time. The EVE data (yellow) overlays the WHI 2008 reference spectrum of the Sun. Markers along the bottom indicate wavelength coverage for other SDO instruments such as EVE/SAM imager, AIA, and HMI.
Credits
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center Scientific Visualization Studio
-
Animator
- Tom Bridgman (Global Science and Technology, Inc.)
-
Producers
- Scott Wiessinger (USRA)
- Genna Duberstein (USRA)
-
Scientist
- Phil Chamberlin (NASA/GSFC)
Release date
This page was originally published on Tuesday, November 20, 2012.
This page was last updated on Sunday, January 19, 2025 at 10:09 PM EST.
Missions
This page is related to the following missions:Series
This page can be found in the following series:Datasets used
-
SSI (Ultraviolet Spectral Solar Irradiance) [SDO: EVE]
ID: 762 -
WHI 2008 (Solar Spectral Irradiance Reference Spectra)
ID: 765
Note: While we identify the data sets used on this page, we do not store any further details, nor the data sets themselves on our site.