A newer version of this visualization is available.
GRACE Detects Brazil Drought
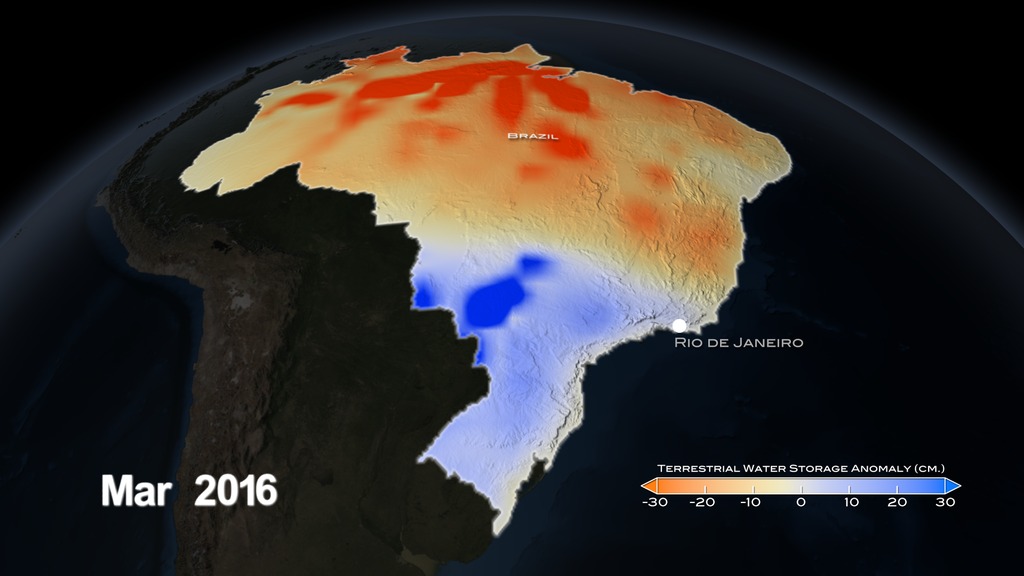
Example animation showing significant ground water storage loss around Brazil's most populated areas. This animation starts with a global view of the Americas, then zooms into the country of Brazil. The location of major reservoirs are revealed, followed by population data. Lastly, GRACE water storage anomaly data for the months of April, May, June is shown beginning in 2002 and going up to 2014. Finally, the region around São Paulo and Rio de Janeiro is highlighted to show the significant water storage loss in this highly populated region.
This video is also available on our YouTube channel.
GRACE (Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment) maps variations in Earth's gravity field. GRACE consists of two identical spacecraft that fly about 220 kilometers (137 miles) apart in a polar orbit 500 kilometers (310 miles) above Earth. GRACE maps Earth's gravity field by making accurate measurements of the distance between the two satellites, using GPS and a microwave ranging system. It is providing scientists from all over the world with an efficient and cost-effective way to map Earth's gravity field with unprecedented accuracy. The results from this mission are yielding crucial information about the distribution and flow of mass within Earth and its surroundings.
The gravity variations studied by GRACE can be used to determine ground water storage on land masses. By comparing current data to an average over time, scientists can generate an anomaly map to see where ground water storage has been depleted or increased.
GRACE is a joint partnership between the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) in the United States and Deutsche Forschungsanstalt für Luft und Raumfahrt (DLR) in Germany. Project management and systems engineering activities are carried out by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory.

Water Storage Anomaly Colorbar for the months of April, May, and June. Orange indicates areas below average and shades of blue are above average water storage.

Print resolution still of Brazil's April through June 2012 water storage anomaly.

Print resolution still of Brazil's April through June 2013 water storage anomaly.

Print resolution still of Brazil's April through June 2014 water storage anomaly.

Print resolution still of Brazil's April through June 2012 water storage anomaly, along with reservoir locations, population data, state zones, major cities, nearby countries, and GRACE anomaly data color bar.

Print resolution still of Brazil's April through June 2013 water storage anomaly, along with reservoir locations, population data, state zones, major cities, nearby countries, and GRACE anomaly data color bar.

Print resolution still of Brazil's April through June 2014 water storage anomaly, along with reservoir locations, population data, state zones, major cities, nearby countries, and GRACE anomaly data color bar.

Mask of Brazil's South east region containing Minas Gerais, São Paulo, Espirito do Santo, and Rio de Janeiro. This alpha texture element can be used in post production to highlight the Southeast region of Brazil.
Credits
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio
-
Visualizer
- Alex Kekesi (Global Science and Technology, Inc.)
-
Producers
- Joy Ng (USRA)
- Kayvon Sharghi (USRA)
-
Scientist
- Augusto Getirana (ORAU)
Release date
This page was originally published on Friday, October 30, 2015.
This page was last updated on Sunday, January 5, 2025 at 10:47 PM EST.
Missions
This page is related to the following missions:Series
This page can be found in the following series:Datasets used
-
TWS Anomaly (Terrestrial Water Storage Anomaly) [Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE)]
ID: 889
Note: While we identify the data sets used on this page, we do not store any further details, nor the data sets themselves on our site.