Exploring the Ionosphere: The View from GOLD
Closeup view of Earth from the perspective of the GOLD instrument. This version interpolates the IRI model to a higher time cadence for a smoother animation.
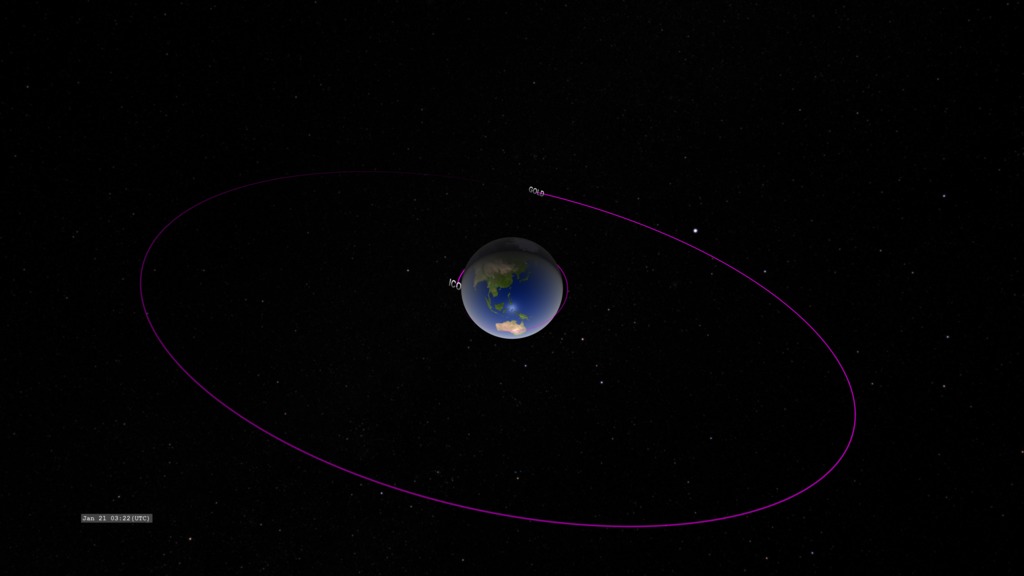
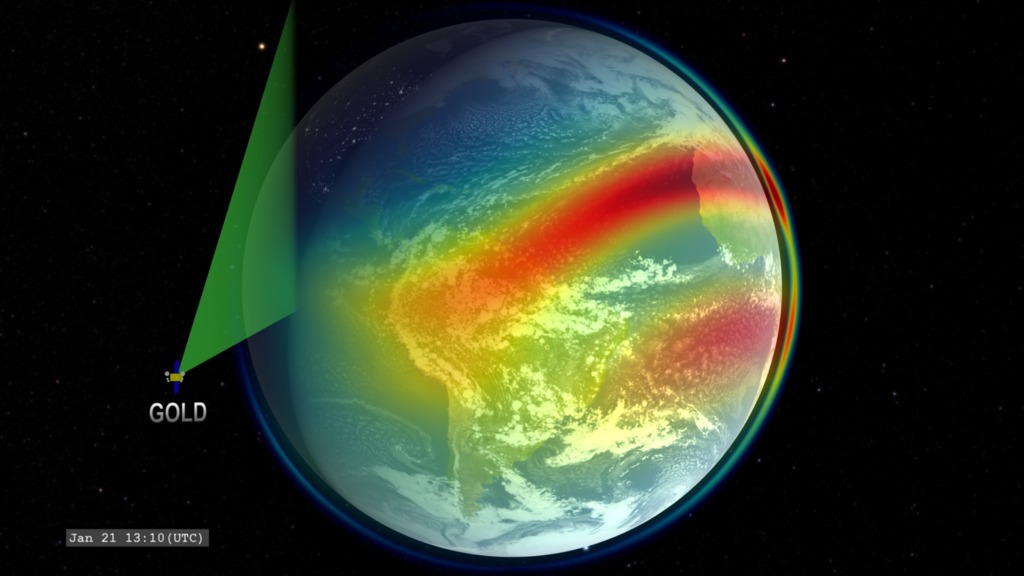
A view of Earth from the point-of-view of the GOLD (Global-scale Observations of the Limb and Disk) instrument in geostationary orbit. This mission will conduct measurements of ionospheric composition to better understand the connection between space weather and its terrestrial impacts.
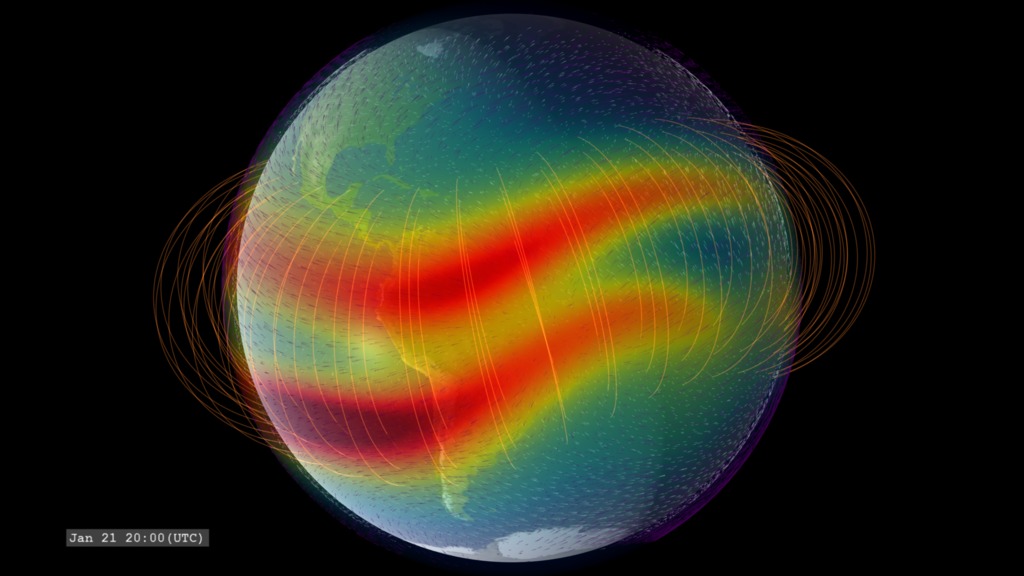
ICON (Ionospheric Connections Explorer) orbits much closer to Earth. The colors over Earth represent model data from the IRI (International Reference Ionosphere) model of the density of the singly-ionized oxygen atom at an altitude of 350 kilometers. Red represents high density. The ion density is enhanced above and below the geomagnetic equator (not perfectly aligned with the geographic equator) on the dayside due to the ionizing effects of solar ultraviolet radiation combined with the effects of high-altitude winds and the geomagnetic field. This ion density decreases at night as the ions recombine with free electrons. At the limb of Earth, we present a cross-sectional profile of the density enhancement.
Closeup view of Earth from the perspective of the GOLD instrument.

Color bar of singly-ionized atomic oxygen density.
Closeup view of Earth from the perspective of the GOLD instrument. This version has no satellites.
For More Information
See NASA.gov
Credits
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio
-
Visualizer
- Tom Bridgman (Global Science and Technology, Inc.)
-
Scientists
- Jeff Klenzing
- Sarah L. Jones (NASA/GSFC)
-
Writer
- Sarah Frazier (ADNET Systems, Inc.)
-
Producer
- Genna Duberstein (USRA)
-
Technical support
- Laurence Schuler (ADNET Systems, Inc.)
- Ian Jones (ADNET Systems, Inc.)
Release date
This page was originally published on Thursday, October 27, 2016.
This page was last updated on Sunday, March 2, 2025 at 10:34 PM EST.
Missions
This page is related to the following missions:Series
This page can be found in the following series:Datasets used
-
IRI 2016 (International Reference Ionosphere)
ID: 944
Note: While we identify the data sets used on this page, we do not store any further details, nor the data sets themselves on our site.

![Complete transcript available.Music credits: 'Faint Glimmer' by Andrew John Skeet [PRS], Andrew Michael Britton [PRS], David Stephen Goldsmith [PRS], 'Ocean Spirals' by Andrew John Skeet [PRS], Andrew Michael Britton [PRS], David Stephen Goldsmith [PRS] from Killer Tracks.Watch this video on the NASA Goddard YouTube channel.](/vis/a010000/a012800/a012817/GOLDOverview_YouTube.00001_print.jpg)