Lucy mission trajectory
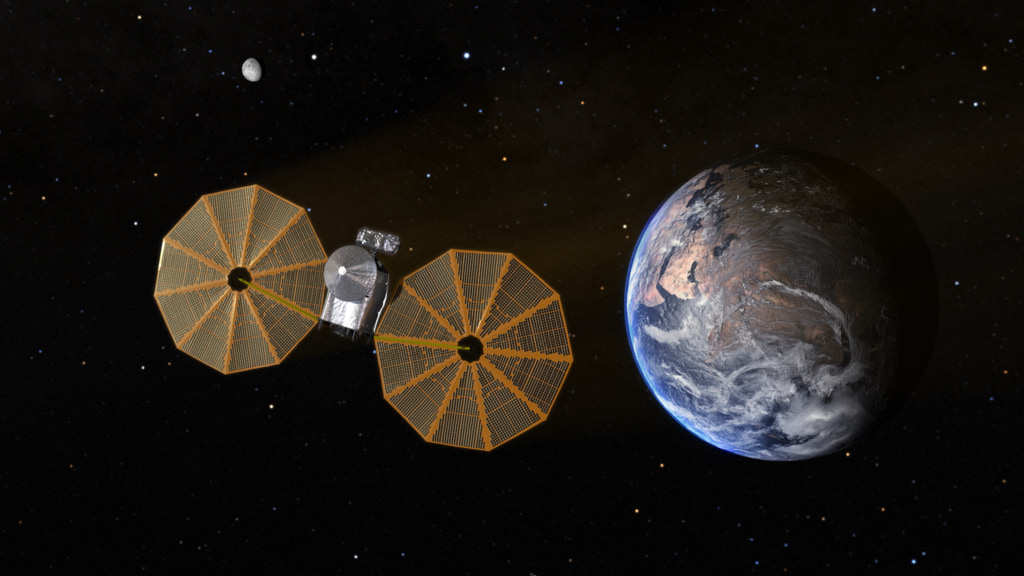
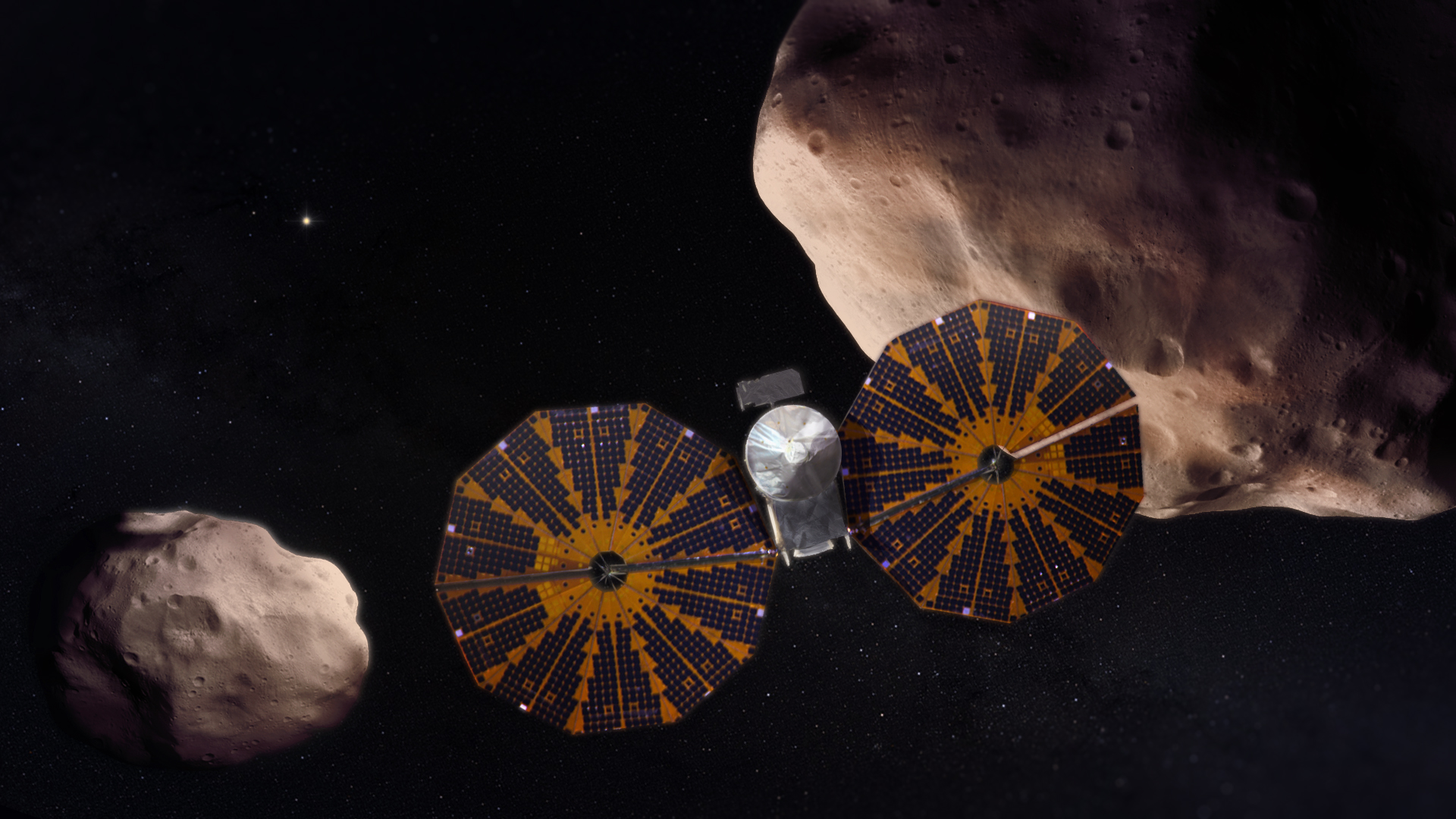
Jupiter's swarms of Trojan asteroids may be remnants of the primordial material that formed the outer planets, and serve as time capsules from the birth of our Solar System more than 4 billion years ago. The Trojans orbit in two loose groups that orbit the Sun, with one group always ahead of Jupiter in its path, the other always behind. At these two Lagrange points the bodies are stabilized by the Sun and Jupiter in a gravitational balancing act. These primitive bodies hold vital clues to deciphering the history of the solar system, and perhaps even the origins of life and organic material on Earth.
Lucy will be the first space mission to study the Trojans. The mission takes its name from the fossilized human ancestor (called “Lucy” by her discoverers) whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution. Likewise, the Lucy mission will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system.
Lucy will launch in October 2021 and, with boosts from Earth's gravity, will complete a twelve-year journey to eight different asteroids — a Main Belt asteroid and seven Jupiter Trojans, the last two members of a “two-for-the-price-of-one” binary system. Lucy’s complex path will take it to both clusters of Trojans and give us our first close-up view of all three major types of bodies in the swarms (so-called C-, P- and D-types).
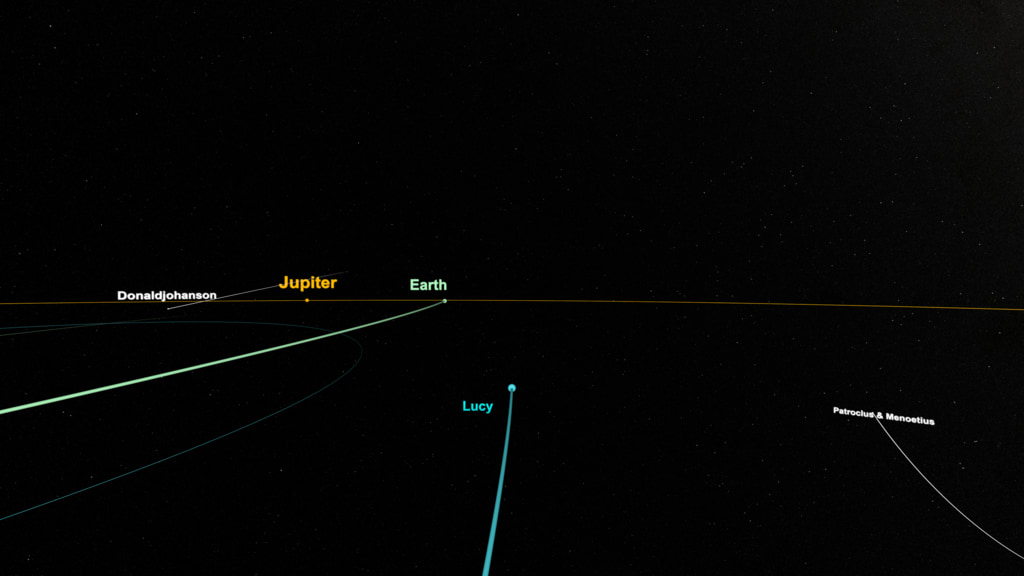
This top-down, solar system view shows the entire Lucy mission in a Jupiter-rotating reference frame. In this reference frame, Jupiter appears fixed in space. Two large regions of asteroids are depicted along Jupiter’s orbit (know as the Jupiter Trojan Asteroids).
Green - Earth
Blue - Lucy
Orange - Jupiter
White - Target, ‘fly-by’ asteroids
This top-down, solar system view shows the entire Lucy mission in a Jupiter-rotating reference frame. In this reference frame, Jupiter appears fixed in space. Two large regions of asteroids are depicted along Jupiter’s orbit (know as the Jupiter Trojan Asteroids). Labels appear as each fly-by occurs.
Green - Earth
Blue - Lucy
Orange - Jupiter
White - Target, ‘fly-by’ asteroids
This video is also available on our YouTube channel.
This is a view of the inner solar system in a Jupiter-rotating reference frame. The camera begins at viewpoint oblique to the ecliptic plane, then moves up to a top-down view.
This top-down, solar system view shows the entire Lucy mission in a Jupiter-rotating reference frame. In this version, the camera pushes into the final asteroid fly-by, 617 Patroclus.
This top-down, solar system view shows the entire Lucy mission in a Jupiter-rotating reference frame. In this version, the camera pushes into the final asteroid fly-by, 617 Patroclus (labeled).
This visualization includes multiple views of the entire Lucy mission in a Jupiter-rotating reference frame. The visualization includes top-down, side, and oblique views of the solar system.
This video is also available on our YouTube channel.
Oblique view of the entire Lucy mission in a Jupiter-rotating reference frame.
Side view of the entire Lucy mission in a Jupiter-rotating reference frame.
Top view of the entire Lucy mission in a Jupiter-rotating reference frame.
Credits
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio
-
Visualizers
- Kel Elkins (USRA)
- Ernie Wright (USRA)
-
Producer
- Dan Gallagher (USRA)
Release date
This page was originally published on Monday, October 21, 2019.
This page was last updated on Monday, April 21, 2025 at 12:15 AM EDT.
Datasets used
-
SPICE Ephemerides (SPICE Ephemerides)
ID: 755Satellite and planetary ephemerides
See all pages that use this dataset
Note: While we identify the data sets used on this page, we do not store any further details, nor the data sets themselves on our site.


![Lucy’s flyby of main-belt asteroid 52246 Donaldjohanson will provide the first close look at this surviving remnant of the solar system’s chaotic past.Complete transcript available.Universal Production Music: “Nico’s Journey” by Nicholas Smith [PRS]; “Knowing Half the Future” and “Temporal Timings” by Lee John Gretton [PRS]; “Poly Propulsion” by Alfie Solo [PRS] Watch this video on the NASA Goddard YouTube channel.](/vis/a010000/a014800/a014821/Lucy_DJ_Preview_Thumbnail_V3.png)



