LISA Pathfinder vs Solar System Dust
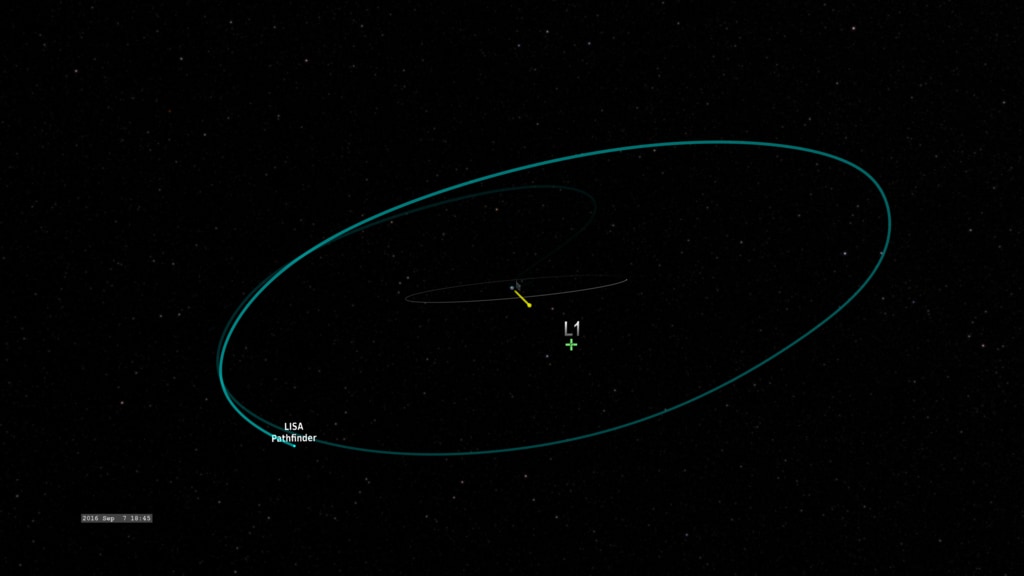
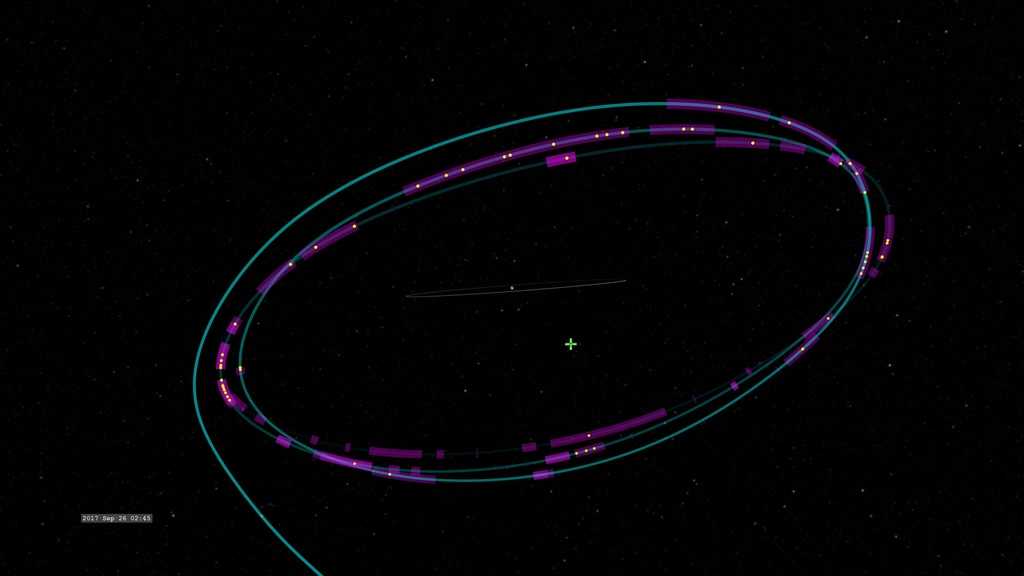
Trajectory of the LISA Pathfinder mission from Earth orbit to its L1 halo orbit including impacts with inner solar system dust (yellow points) and time windows along the orbit when this capability is enabled (purple). With labels.
LISA Pathfinder, a mission led by ESA (the European Space Agency) that included NASA contributions, successfully demonstrated technologies needed to build a future space-based gravitational wave observatory, a tool for detecting ripples in space-time produced by, among other things, merging black holes. A team of NASA scientists leveraged LISA Pathfinder's record-setting sensitivity to map microscopic dust shed by comets and asteroids.
These animations follow the trajectory of LISA Pathfinder from Earth to its working "halo" orbit around Sun-Earth L1, a gravitational balance point about 930,000 miles (1.5 million kilometers) from Earth in the sun's direction, and show the locations of 54 dust impacts detected during the mission.
Trajectory of the LISA Pathfinder mission from Earth orbit to its L1 halo orbit including impacts with inner solar system dust (yellow points) and time windows along the orbit when this capability is enabled (purple). Without labels.
Trajectory of the LISA Pathfinder mission in a heliocentric frame, including impacts with inner solar system dust (yellow points) and time windows along the orbit when this capability is enabled (purple). With labels.
Trajectory of the LISA Pathfinder mission in a heliocentric frame, including impacts with inner solar system dust (yellow points) and time windows along the orbit when this capability is enabled (purple). Without labels.
Credits
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio
-
Data visualizer
- Tom Bridgman (Global Science and Technology, Inc.)
-
Scientist
- James Ira Thorpe (NASA/GSFC)
-
Writer
- Francis Reddy (University of Maryland College Park)
-
Producer
- Scott Wiessinger (USRA)
Release date
This page was originally published on Monday, November 18, 2019.
This page was last updated on Sunday, February 2, 2025 at 10:42 PM EST.
Related papers
Datasets used
-
SPICE Ephemerides (SPICE Ephemerides)
ID: 755Satellite and planetary ephemerides
See all pages that use this dataset
Note: While we identify the data sets used on this page, we do not store any further details, nor the data sets themselves on our site.