Darwin Model of Ocean Microbes Updated
Left: Older Darwin model of global ocean microbiome showing no drop-off of Prochlorococcus populations in arctic regions.
Right: New Darwin model, updated to show interactions between heterotrophic bacteria and shared grazer, which prevents Prochlorococcus habitat extending poleward.
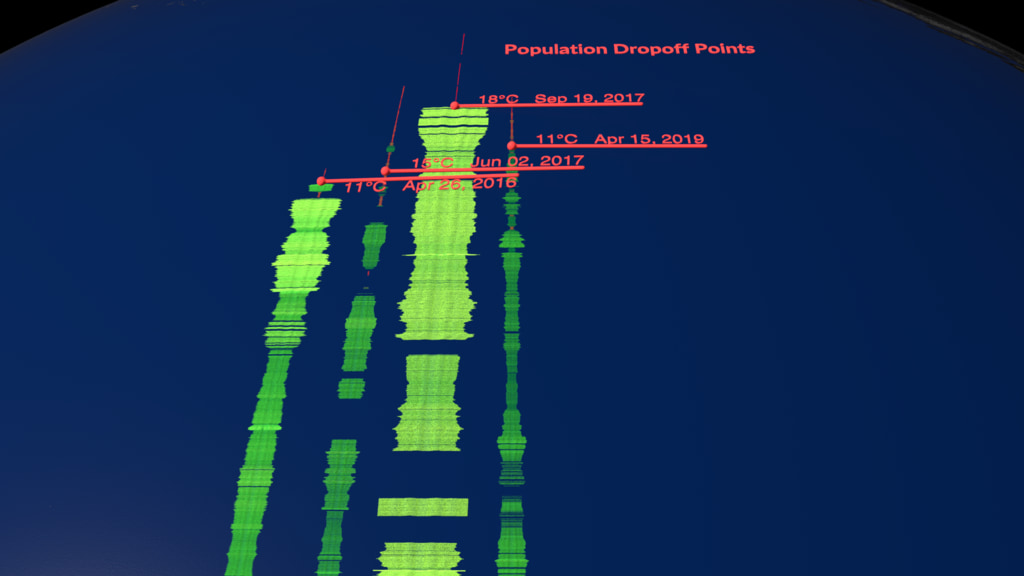
Research ships traveling from Hawaii into the north Pacific Ocean have measured quantities of tiny organisms in the water called Prochlorococcus using an instrument called SeaFlow. These organisms are phytoplankton that, like plants, turn carbon dioxide into oxygen. Prochlorococcus is both the smallest and most abundant photosynthesizing organism on the planet. Scientists observed a falloff in the quantity of these organisms as the ships moved northward; however, the falloff did not happen where the water cooled as the scientists expected. This was a bit of a mystery. The scientists hypothesized that the drop off was actually due to competition with other tiny organisms like copiotrophic bacteria and their shared predator Paraphysomonas_sp, a type of zooplankton. They coded this hypothesis into an existing computational model of the oceans called Darwin. Sure enough, in the new version of the computational model that included the predator-prey relationship, the drop off occurred in the same place as the real-world measurements. This model can be used to understand how carbon is absorbed from the atmosphere over all of the world's oceans. This demonstrates the power of scientific research that combines observed data and model data.
Credits
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio
-
Visualizer
- Andrew J Christensen (SSAI)
-
Scientists
- Stephanie Dutkiewicz (Massachusetts Institute of Technology)
- Christopher Follett (Massachusetts Institute of Technology)
- Francois Ribalet (University of Washington)
-
Technical support
- Laurence Schuler (ADNET Systems, Inc.)
- Ian Jones (ADNET Systems, Inc.)
Release date
This page was originally published on Wednesday, April 13, 2022.
This page was last updated on Thursday, October 10, 2024 at 12:13 AM EDT.
Related papers
Datasets used
-
SeaFlow datasets v1.3 (doi10.5281/zenodo.3994953) [ship: SeaFlow]
ID: 1140SeaFlow is an underway flow cytometer that provides continuous shipboard observations of the abundance and optical properties of small phytoplankton (<5 μm in equivalent spherical diameter, ESD).
Credit: Annette Hynes, Chris Berthiaume, Francois Ribalet, E Virginia Armbrust
This dataset can be found at: https://seaflow.netlify.app/
See all pages that use this dataset -
Darwin
ID: 1141The Darwin Project is an initiative to advance the development and application of novel models of marine microbes and microbial communities, identifying the relationships of individuals and communities to their environment, connecting cellular-scale processes to global microbial community structure.
Credit: Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation, Simons Foundation, NSF, NASA
This dataset can be found at: https://darwinproject.mit.edu/
See all pages that use this dataset
Note: While we identify the data sets used on this page, we do not store any further details, nor the data sets themselves on our site.